Early Adverse Events predict Survival Outcomes in HER2-positive Advanced Breast Cancer Patients treated with Lapatinib plus Capecitabine
- PMID: 32231738
- PMCID: PMC7097941
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.41996
Early Adverse Events predict Survival Outcomes in HER2-positive Advanced Breast Cancer Patients treated with Lapatinib plus Capecitabine
Abstract
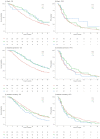
Background: This study aimed to investigate the impact of early adverse events (AE) following the initiation of lapatinib plus capecitabine on the progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) outcomes of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) positive advanced breast cancer (ABC) patients. Methods: A secondary analysis of participants treated with lapatinib plus capecitabine, or ado-trastuzumab emtansine in the clinical trial EMILIA was conducted. Cox proportional hazard analysis was used to assess the impact of AE occurring within the first 42 days of lapatinib plus capecitabine therapy on the PFS and OS outcomes of ABC patients. Results: The study included 488 HER2-positive (ABC) patients initiated on lapatinib plus capecitabine. Rash (Hazard Ratio (HR) [95% Confidence Interval (CI)]: Grade 1 = 0.67 [0.46-0.98], Grade 2+ = 0.71 [0.42-1.19]; p = 0.046) and hand-foot syndrome (HR [95% CI]: Grade 1 = 0.58 [0.43-0.80], Grade 2+ = 0.61 [0.43-0.86]; p = <0.001) occurring within the first 42 days of lapatinib plus capecitabine therapy were significantly associated with improved OS. Conversely, nausea and vomiting occurring within the first 42 days of lapatinib plus capecitabine therapy was significantly associated with worsened OS (HR [95% CI]: Grade 1 = 1.08 [0.82-1.42], Grade 2+ = 1.52 [1.13-2.03]; p = 0.027). Conclusions: Rash and hand-foot syndrome occurring early after the initiation of on lapatinib plus capecitabine were significantly associated with improved OS, while early nausea and vomiting was associated with worse OS. In HER2-positive ABC patients initiating lapatinib plus capecitabine, consideration should be given to more closely monitoring patients at risk of nausea and vomiting, while rash and hand foot syndrome are AE associated with improved survival.
Keywords: adverse events; breast neoplasms; capecitabine; hand-foot syndrome; lapatinib; survival analysis.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: M.J.S., R.A.M. and A.R. report grants from Pfizer, outside the scope of the submitted work. The authors have no other conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Trastuzumab emtansine versus capecitabine plus lapatinib in patients with previously treated HER2-positive advanced breast cancer (EMILIA): a descriptive analysis of final overall survival results from a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2017 Jun;18(6):732-742. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30312-1. Epub 2017 May 16. Lancet Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28526536 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Lapatinib plus capecitabine for HER2-positive advanced breast cancer: a multicentre study of Anatolian Society of Medical Oncology (ASMO).J Chemother. 2014 Oct;26(5):300-5. doi: 10.1179/1973947813Y.0000000147. Epub 2013 Dec 6. J Chemother. 2014. PMID: 24112786
-
A phase two randomised trial of neratinib monotherapy versus lapatinib plus capecitabine combination therapy in patients with HER2+ advanced breast cancer.Eur J Cancer. 2013 Dec;49(18):3763-72. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2013.07.142. Epub 2013 Aug 15. Eur J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23953056 Clinical Trial.
-
Lapatinib: a dual inhibitor of human epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases.Clin Ther. 2008 Aug;30(8):1426-47. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2008.08.008. Clin Ther. 2008. PMID: 18803986 Review.
-
Lapatinib for the treatment of HER2-overexpressing breast cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2009 Oct;13 Suppl 3:1-6. doi: 10.3310/hta13suppl3/01. Health Technol Assess. 2009. PMID: 19846022 Review.
Cited by
-
Survival Outcomes of Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated with Afatinib Who Are Affected by Early Adverse Events.J Oncol. 2021 Jun 16;2021:2414897. doi: 10.1155/2021/2414897. eCollection 2021. J Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34221011 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Factors Influencing Progression-Free Survival in HER2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients Who Were Treated With A Combination of Lapatinib and Capecitabine.Eur J Breast Health. 2023 Apr 1;19(2):128-133. doi: 10.4274/ejbh.galenos.2023.2022-12-4. eCollection 2023 Apr. Eur J Breast Health. 2023. PMID: 37025570 Free PMC article.
-
Her2 positive metastatic breast cancer treated with low dose lapatinib in a resource-constrained setting in South India: a retrospective audit.Ecancermedicalscience. 2024 Sep 6;18:1758. doi: 10.3332/ecancer.2024.1758. eCollection 2024. Ecancermedicalscience. 2024. PMID: 39430084 Free PMC article.
-
Adverse Drug Reactions with HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Treatment: An Analysis from the Italian Pharmacovigilance Database.Drugs Real World Outcomes. 2022 Mar;9(1):91-107. doi: 10.1007/s40801-021-00278-z. Epub 2021 Sep 15. Drugs Real World Outcomes. 2022. PMID: 34528216 Free PMC article.
-
Early Adverse Event Derived Biomarkers in Predicting Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treated with Immunotherapy.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 28;15(9):2521. doi: 10.3390/cancers15092521. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37173987 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Giordano SH, Temin S, Chandarlapaty S, Crews JR, Esteva FJ, Kirshner JJ. et al. Systemic Therapy for Patients With Advanced Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Positive Breast Cancer: ASCO Clinical Practice Guideline Update. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36:2736–40. - PubMed
-
- Medina PJ, Goodin S. Lapatinib: a dual inhibitor of human epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases. Clin Ther. 2008;30:1426–47. - PubMed
-
- Walko CM, Lindley C. Capecitabine: a review. Clin Ther. 2005;27:23–44. - PubMed
-
- Petrelli F, Ghidini M, Lonati V, Tomasello G, Borgonovo K, Ghilardi M. et al. The efficacy of lapatinib and capecitabine in HER-2 positive breast cancer with brain metastases: A systematic review and pooled analysis. Eur J Cancer. 2017;84:141–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous