Discovery of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma-Related Aberrant Glycosylations: A Multilateral Approach of Lectin Microarray-Based Tissue Glycomic Profiling With Public Transcriptomic Datasets
- PMID: 32232009
- PMCID: PMC7082313
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00338
Discovery of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma-Related Aberrant Glycosylations: A Multilateral Approach of Lectin Microarray-Based Tissue Glycomic Profiling With Public Transcriptomic Datasets
Abstract
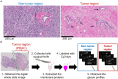
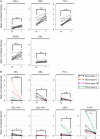
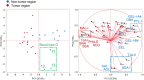
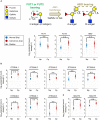
Aberrant protein glycosylation is one of the most notable features in cancerous tissues, and thereby glycoproteins with disease-relevant glycosylation alterations are fascinating targets for the development of biomarkers and therapeutic agents. For this purpose, a reliable strategy is needed for the analysis of glycosylation alterations occurring on specific glycoproteins during the progression of cancer. Here, we propose a bilateral approach combining lectin microarray-based tissue glycomic profiling and database-derived transcriptomic datasets. First, lectin microarray was used to perform differential glycomic profiling of crude extracts derived from non-tumor and tumor regions of frozen tissue sections from pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). This analysis revealed two notable tissue glycome alterations in PDAC samples: increases in sialylated glycans and bisecting N-acetylglucosamine and a decrease in ABO blood group antigens. To examine aberrations in the glycosylation machinery related to these glycomic alterations, we next employed public datasets of gene expression profiles in cancerous and normal pancreases provided by The Cancer Genome Atlas and the Genotype-Tissue Expression projects, respectively. In this analysis, glycosyltransferases responsible for the glycosylation alterations showed aberrant gene expression in the cancerous tissues, consistent with the tissue glycomic profiles. The correlated alterations in glycosyltransferase expression and tissue glycomics were then evaluated by differential glycan profiling of a membrane N-glycoprotein, basigin, expressed in tumor and non-tumor pancreatic cells. The focused differential glycomic profiling for endogenous basigin derived from non-tumor and cancerous regions of PDAC tissue sections demonstrated that PDAC-relevant glycan alterations of basigin closely reflected the notable features in the disease-specific alterations in the tissue glycomes. In conclusion, the present multi-omics strategy using public transcriptomic datasets and experimental glycomic profiling using a tiny amount of clinical specimens successfully demonstrated that basigin is a representative N-glycoprotein that reflects PDAC-related aberrant glycosylations. This study indicates the usefulness of large public data sets such as the gene expression profiles of glycosylation-related genes for evaluation of the highly sensitive tissue glycomic profiling results. This strategy is expected to be useful for the discovery of novel glyco-biomarkers and glyco-therapeutic targets.
Keywords: ABO blood group antigen; Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx); The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA); basigin/CD147; glycosylation; glycosyltransferase; lectin microarray; multi-omics.
Copyright © 2020 Wagatsuma, Nagai-Okatani, Matsuda, Masugi, Imaoka, Yamazaki, Sakamoto and Kuno.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tissue Glycome Mapping: Lectin Microarray-Based Differential Glycomic Analysis of Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissue Sections.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2460:161-180. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2148-6_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34972936
-
LM-GlycomeAtlas Ver. 1.0: A Novel Visualization Tool for Lectin Microarray-Based Glycomic Profiles of Mouse Tissue Sections.Molecules. 2019 Aug 15;24(16):2962. doi: 10.3390/molecules24162962. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31443278 Free PMC article.
-
A glycosyltransferase gene signature to detect pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients with poor prognosis.EBioMedicine. 2021 Sep;71:103541. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103541. Epub 2021 Aug 20. EBioMedicine. 2021. PMID: 34425307 Free PMC article.
-
Sweet systems: technologies for glycomic analysis and their integration into systems biology.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2021 Jun;56(3):301-320. doi: 10.1080/10409238.2021.1908953. Epub 2021 Apr 5. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33820453 Review.
-
Clinical applications of glycomic approaches for the detection of cancer and other diseases.Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2006 Dec;8(6):507-13. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2006. PMID: 17243486 Review.
Cited by
-
Cancer glycomics offers potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets in the framework of 3P medicine.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 22;13:970489. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.970489. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36072925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expanding the recognition of monosaccharides and glycans: A comprehensive analytical approach using chemical-nose/tongue technology and a comparison to lectin microarrays.BBA Adv. 2024 Dec 8;7:100129. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadva.2024.100129. eCollection 2025. BBA Adv. 2024. PMID: 39790466 Free PMC article.
-
Role of tumor cell sialylation in pancreatic cancer progression.Adv Cancer Res. 2023;157:123-155. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2022.07.003. Epub 2022 Sep 27. Adv Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 36725107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of Mesothelin Glycosylation in Pancreatic Cancer: Decreased Core Fucosylated Glycoforms in Pancreatic Cancer Patients' Sera.Biomedicines. 2022 Aug 10;10(8):1942. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10081942. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36009489 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Mass Spectrometry-Based Glycomic and Glycoproteomic Studies of Pancreatic Diseases.Front Chem. 2021 Jul 23;9:707387. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.707387. eCollection 2021. Front Chem. 2021. PMID: 34368082 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Varki A, III, Cummings RD, Esko JD, Stanley P, Hart GW, Aebi M, et al. Essentials of Glycobiology. New York, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; (2015). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

