Circadian Regulation of Immunity Through Epigenetic Mechanisms
- PMID: 32232012
- PMCID: PMC7082642
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00096
Circadian Regulation of Immunity Through Epigenetic Mechanisms
Abstract
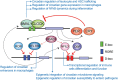
The circadian clock orchestrates daily rhythms in many physiological, behavioral and molecular processes, providing means to anticipate, and adapt to environmental changes. A specific role of the circadian clock is to coordinate functions of the immune system both at steady-state and in response to infectious threats. Hence, time-of-day dependent variables are found in the physiology of immune cells, host-parasite interactions, inflammatory processes, or adaptive immune responses. Interestingly, the molecular clock coordinates transcriptional-translational feedback loops which orchestrate daily oscillations in expression of many genes involved in cellular functions. This clock function is assisted by tightly controlled transitions in the chromatin fiber involving epigenetic mechanisms which determine how a when transcriptional oscillations occur. Immune cells are no exception, as they also present a functional clock dictating transcriptional rhythms. Hereby, the molecular clock and the chromatin regulators controlling rhythmicity represent a unique scaffold mediating the crosstalk between the circadian and the immune systems. Certain epigenetic regulators are shared between both systems and uncovering them and characterizing their dynamics can provide clues to design effective chronotherapeutic strategies for modulation of the immune system.
Keywords: chromatin; circadian rhythm; epigenetics; infection; transcriptional regulation.
Copyright © 2020 Orozco-Solis and Aguilar-Arnal.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Circadian rhythms in the three-dimensional genome: implications of chromatin interactions for cyclic transcription.Clin Epigenetics. 2019 May 15;11(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s13148-019-0677-2. Clin Epigenetics. 2019. PMID: 31092281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromatin landscape and circadian dynamics: Spatial and temporal organization of clock transcription.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Jun 2;112(22):6863-70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1411264111. Epub 2014 Nov 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25378702 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic control of circadian clocks by environmental signals.Trends Cell Biol. 2024 Dec;34(12):992-1006. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2024.02.005. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Trends Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38423855 Review.
-
Spatiotemporal chromatin dynamics - A telltale of circadian epigenetic gene regulation.Life Sci. 2019 Mar 15;221:377-391. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.02.006. Epub 2019 Feb 2. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30721705 Review.
-
Transcriptional Control of Circadian Rhythms and Metabolism: A Matter of Time and Space.Endocr Rev. 2020 Oct 1;41(5):707-32. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnaa014. Endocr Rev. 2020. PMID: 32392281 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Light Environment Influences Developmental Programming of the Metabolic and Visual Systems in Mice.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021 Apr 1;62(4):22. doi: 10.1167/iovs.62.4.22. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021. PMID: 33861321 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional dynamics in type 2 diabetes progression is linked with circadian, thermogenic, and cellular stress in human adipose tissue.Commun Biol. 2025 Mar 8;8(1):398. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-07709-5. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 40057615 Free PMC article.
-
Microglial clock dysfunction during neuroinflammation impairs oligodendrocyte progenitor cell recruitment and disrupts neuroimmune homeostasis.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 7;16:1620343. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1620343. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40692797 Free PMC article.
-
The balance between protective and pathogenic immune responses to pneumonia in the neonatal lung is enforced by gut microbiota.Sci Transl Med. 2022 Jun 15;14(649):eabl3981. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abl3981. Epub 2022 Jun 15. Sci Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35704600 Free PMC article.
-
Controllable and Uncontrollable Stress Differentially Impact Fear Conditioned Alterations in Sleep and Neuroimmune Signaling in Mice.Life (Basel). 2022 Aug 26;12(9):1320. doi: 10.3390/life12091320. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36143359 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

