Realizing flexible bioelectronic medicines for accessing the peripheral nerves - technology considerations
- PMID: 32232084
- PMCID: PMC7098212
- DOI: 10.1186/s42234-018-0010-y
Realizing flexible bioelectronic medicines for accessing the peripheral nerves - technology considerations
Abstract
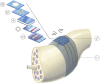
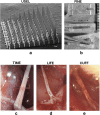
Patients suffering from conditions such as paralysis, diabetes or rheumatoid arthritis could in the future be treated in a personalised manner using bioelectronic medicines (BEms) (Nat Rev Drug Discov 13:399-400, 2013, Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:8284-9, 2016, J Intern Med 282:37-45, 2017). To deliver this personalised therapy based on electricity, BEms need to target various sites in the human body and operate in a closed-loop manner. The specific conditions and anatomy of the targeted sites pose unique challenges in the development of BEms. With a focus on BEms based on flexible substrates for accessing small peripheral nerves, this paper discusses several system-level technology considerations related to the development of such devices. The focus is mainly on miniaturisation and long-term operation. We present an overview of common substrate and electrode materials, related processing methods, and discuss assembly, miniaturisation and long-term stability issues.
© The Author(s) 2018.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Banda C, Johnson RW, Zhang T, Hou Z, Charles HK. Flip chip assembly of thinned silicon die on flex substrates. IEEE Trans Electron Pa M. 2008;31:1–8. doi: 10.1109/TEPM.2007.914217. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
