Diabetes is a risk factor for the progression and prognosis of COVID-19
- PMID: 32233013
- PMCID: PMC7228407
- DOI: 10.1002/dmrr.3319
Diabetes is a risk factor for the progression and prognosis of COVID-19
Abstract
Backgound: To figure out whether diabetes is a risk factor influencing the progression and prognosis of 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19).
Methods: A total of 174 consecutive patients confirmed with COVID-19 were studied. Demographic data, medical history, symptoms and signs, laboratory findings, chest computed tomography (CT) as well the treatment measures were collected and analysed.
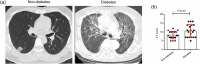
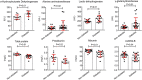
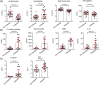
Results: We found that COVID-19 patients without other comorbidities but with diabetes (n = 24) were at higher risk of severe pneumonia, release of tissue injury-related enzymes, excessive uncontrolled inflammation responses and hypercoagulable state associated with dysregulation of glucose metabolism. Furthermore, serum levels of inflammation-related biomarkers such as IL-6, C-reactive protein, serum ferritin and coagulation index, D-dimer, were significantly higher (P < .01) in diabetic patients compared with those without, suggesting that patients with diabetes are more susceptible to an inflammatory storm eventually leading to rapid deterioration of COVID-19.
Conclusions: Our data support the notion that diabetes should be considered as a risk factor for a rapid progression and bad prognosis of COVID-19. More intensive attention should be paid to patients with diabetes, in case of rapid deterioration.
Keywords: COVID-19; diabetes; prognosis.
© 2020 The Authors. Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest regarding this publication.
Figures
Comment in
-
Technology Gap Deepened by Coronavirus Pandemic.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2020 Jul;14(4):774-775. doi: 10.1177/1932296820929390. Epub 2020 May 27. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2020. PMID: 32460626 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Serum amyloid A protein has been undervalued as a biomarker of COVID-19.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2021 Jan;37(1):e3376. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3376. Epub 2020 Jul 18. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2021. PMID: 32588938 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Diabetes and Covid-19: An interplay difficult to dissect.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2021 Jan;37(1):e3387. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3387. Epub 2020 Aug 20. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2021. PMID: 32818297 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Tipnis SR, Hooper NM, Hyde R, Karran E, Christie G, Turner AJ. A human homolog of angiotensin‐converting enzyme. Cloning and functional expression as a captopril‐insensitive carboxypeptidase. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(43):33238‐33243. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

