Functionally heterogeneous human satellite cells identified by single cell RNA sequencing
- PMID: 32234209
- PMCID: PMC7164960
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.51576
Functionally heterogeneous human satellite cells identified by single cell RNA sequencing
Abstract
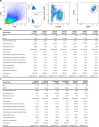
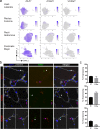
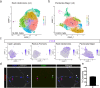
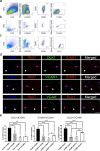
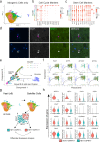
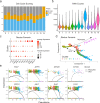
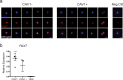
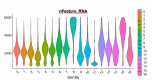
Although heterogeneity is recognized within the murine satellite cell pool, a comprehensive understanding of distinct subpopulations and their functional relevance in human satellite cells is lacking. We used a combination of single cell RNA sequencing and flow cytometry to identify, distinguish, and physically separate novel subpopulations of human PAX7+ satellite cells (Hu-MuSCs) from normal muscles. We found that, although relatively homogeneous compared to activated satellite cells and committed progenitors, the Hu-MuSC pool contains clusters of transcriptionally distinct cells with consistency across human individuals. New surface marker combinations were enriched in transcriptional subclusters, including a subpopulation of Hu-MuSCs marked by CXCR4/CD29/CD56/CAV1 (CAV1+). In vitro, CAV1+ Hu-MuSCs are morphologically distinct, and characterized by resistance to activation compared to CAV1- Hu-MuSCs. In vivo, CAV1+ Hu-MuSCs demonstrated increased engraftment after transplantation. Our findings provide a comprehensive transcriptional view of normal Hu-MuSCs and describe new heterogeneity, enabling separation of functionally distinct human satellite cell subpopulations.
Keywords: Human satellite cell transcriptome; human; human biology; medicine; muscle stem cell; regenerative medicine; satellite cell transplantation; stem cells.
© 2020, Barruet et al.
Conflict of interest statement
EB, SG, KS, JW, SL, LB, AW, SX, ST, AB, JP No competing interests declared
Figures





References
-
- Aguilar CA, Pop R, Shcherbina A, Watts A, Matheny RW, Cacchiarelli D, Han WM, Shin E, Nakhai SA, Jang YC, Carrigan CT, Gifford CA, Kottke MA, Cesana M, Lee J, Urso ML, Meissner A. Transcriptional and chromatin dynamics of muscle regeneration after severe trauma. Stem Cell Reports. 2016;7:983–997. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2016.09.009. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alexander MS, Rozkalne A, Colletta A, Spinazzola JM, Johnson S, Rahimov F, Meng H, Lawlor MW, Estrella E, Kunkel LM, Gussoni E. CD82 is a marker for prospective isolation of human muscle satellite cells and is linked to muscular dystrophies. Cell Stem Cell. 2016;19:800–807. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2016.08.006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alonso-Martin S, Rochat A, Mademtzoglou D, Morais J, de Reyniès A, Auradé F, Chang TH, Zammit PS, Relaix F. Gene expression profiling of muscle stem cells identifies novel regulators of postnatal myogenesis. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology. 2016;4:58. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2016.00058. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

