Cytokine release syndrome in severe COVID-19: interleukin-6 receptor antagonist tocilizumab may be the key to reduce mortality
- PMID: 32234467
- PMCID: PMC7118634
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105954
Cytokine release syndrome in severe COVID-19: interleukin-6 receptor antagonist tocilizumab may be the key to reduce mortality
Abstract
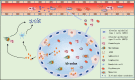
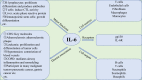
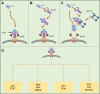
Since December 2019, a viral pneumonia, named coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), from Wuhan, China, has swept the world. Although the case fatality rate is not high, the number of people infected is large and there is still a large number of patients dying. With the collation and publication of more and more clinical data, a large number of data suggest that there are mild or severe cytokine storms in severe patients, which is an important cause of death. Therefore, treatment of the cytokine storm has become an important part of rescuing severe COVID-19 patients. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) plays an important role in cytokine release syndrome. If it is possible to block the signal transduction pathway of IL-6, it is expected to become a new method for the treatment of severe COVID-19 patients. Tocilizumab is an IL-6 receptor (IL-6R) blocker that can effectively block the IL-6 signal transduction pathway and thus is likely to become an effective drug for patients with severe COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cytokine release syndrome; IL-6; IL-6R; Tocilizumab.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
References
-
- Xu Z., Shi L., Wang Y., Zhang J., Huang L., Zhang C. Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet Respir Med. 2020 Feb 18 doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30076-X. [Epub ahead of print]Erratum in: Lancet Respir Med 2020 Feb 25 [Epub ahead of print]. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30085-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Miossec P., Kolls J.K. Targeting IL-17 and TH17 cells in chronic inflammation. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012;11:763–776. - PubMed
-
- Norelli M., Camisa B., Barbiera G., Falcone L., Purevdorj A., Genua M. Monocyte-derived IL-1 and IL-6 are differentially required for cytokine-release syndrome and neurotoxicity due to CAR T cells. Nat Med. 2018;24:739–748. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

