COVID-19, diabetes mellitus and ACE2: The conundrum
- PMID: 32234504
- PMCID: PMC7118535
- DOI: 10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108132
COVID-19, diabetes mellitus and ACE2: The conundrum
Figures
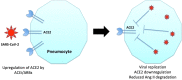
Comment on
-
Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China.N Engl J Med. 2020 Apr 30;382(18):1708-1720. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2002032. Epub 2020 Feb 28. N Engl J Med. 2020. PMID: 32109013 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guan W, Ni Z, Hu Y, Liang W, Ou C, He J, et al. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med [Internet]; 2020 [cited 2020 Mar 20]; Available from: http://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMoa2002032. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and Important Lessons From the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China: Summary of a Report of 72 314 Cases From the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA [Internet]; 2020 [cited 2020 Mar 21]; Available from: https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2762130. - PubMed
-
- Yang X, Yu Y, Xu J, Shu H, Xia J, Liu H, et al. Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study. Lancet Respir Med [Internet]; 2020 [cited 2020 Mar 20]; Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2213260020300795. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wu C, Chen X, Cai Y, Xia J, Zhou X, Xu S, et al. Risk Factors Associated With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Death in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA Intern Med [Internet]; 2020 [cited 2020 Mar 21]; Available from: https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/2763184. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hong K.-W., Cheong H.J., Choi W.S., Lee J., Wie S.-H., Baek J.H. Clinical courses and outcomes of hospitalized adult patients with seasonal influenza in Korea, 2011–2012: Hospital-based Influenza Morbidity & Mortality (HIMM) surveillance. J Infect Chemother. 2014;20:9–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

