Lymphoproliferative disorder in a lung transplant recipient
- PMID: 32234858
- PMCID: PMC7167483
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2020-234532
Lymphoproliferative disorder in a lung transplant recipient
Abstract
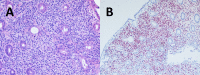
Post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD) is uncommon following solid organ transplantation. We present a case of PTLD presenting as hematochezia and abdominal pain in a 66-year-old man, who had undergone bilateral lung transplantation with alemtuzumab induction 7 months prior to presentation. The transplant serologic status was "high-risk" for the presence of both Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) serologies in the donor and negative serologies in the recipient. Biopsies taken during colonoscopy stained strongly positive for EBV-encoded RNA. Mediastinal lymph node biopsies also showed atypical, EBV-positive lymphohistiocytic infiltration with focal necrosis. The patient's hospital course was complicated by treatment side effects, most notably bowel perforation following rituximab. In this case report the topic of PTLD is reviewed and consideration is given to whether alemtuzumab induction may have contributed to the patient's development of PTLD.
Keywords: immunological products and vaccines; oncology; transplantation.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2020. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Kamholz SL, Veith FJ, Mollenkopf FP, et al. . Single lung transplantation with cyclosporin immunosuppression. evaluation of canine and human recipients. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1983;86:537–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
