Corona Virus (COVID-19) "Infodemic" and Emerging Issues through a Data Lens: The Case of China
- PMID: 32235433
- PMCID: PMC7177854
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17072309
Corona Virus (COVID-19) "Infodemic" and Emerging Issues through a Data Lens: The Case of China
Abstract
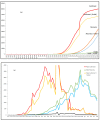
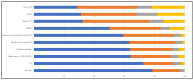
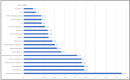
Coronavirus (COVID-19) is a humanitarian emergency, which started in Wuhan in China in early December 2019, brought into the notice of the authorities in late December, early January 2020, and, after investigation, was declared as an emergency in the third week of January 2020. The WHO declared this as Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) on 31th of January 2020, and finally a pandemic on 11th March 2020. As of March 24th, 2020, the virus has caused a casualty of over 16,600 people worldwide with more than 380,000 people confirmed as infected by it, of which more than 10,000 cases are serious. Mainly based on Chinese newspapers, social media and other digital platform data, this paper analyzes the timeline of the key actions taken by the government and people over three months in five different phases. It found that although there was an initial delay in responding, a unique combination of strong governance, strict regulation, strong community vigilance and citizen participation, and wise use of big data and digital technologies, were some of the key factors in China's efforts to combat this virus. Being inviable and non-measurable (unlike radioactive exposure), appropriate and timely information is very important to form the basic foundation of mitigation and curative measures. Infodemic, as it is termed by WHO, is a key word, where different stakeholder's participation, along with stricter regulation, is required to reduce the impact of fake news in this information age and social media. Although different countries will need different approaches, focusing on its humanitarian nature and addressing infodemic issues are the two critical factors for future global mitigation efforts.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus; citizen participation; data science; good governance; humanitarian emergency; infodemic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Mckinsey Coronavirus COVID-19: Facts and Insights. [(accessed on 11 March 2020)]; Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/~/media/mckinsey/business%20functions/risk/our%....
-
- Zaroncostas J. How to Fight an Infodemic. [(accessed on 11 March 2020)]; Available online: www.thelancet.com.
-
- WHO China . Report of the WHO-China Joint Mission on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2019.
-
- Sina News. [(accessed on 11 March 2020)]; Available online: https://news.sina.cn/zt_d/yiqing0121?wm=6122_1221.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

