Mitophagy in the Pathogenesis of Liver Diseases
- PMID: 32235615
- PMCID: PMC7226805
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9040831
Mitophagy in the Pathogenesis of Liver Diseases
Abstract
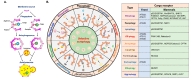
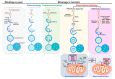
Autophagy is a catabolic process involving vacuolar sequestration of intracellular components and their targeting to lysosomes for degradation, thus supporting nutrient recycling and energy regeneration. Accumulating evidence indicates that in addition to being a bulk, nonselective degradation mechanism, autophagy may selectively eliminate damaged mitochondria to promote mitochondrial turnover, a process termed "mitophagy". Mitophagy sequesters dysfunctional mitochondria via ubiquitination and cargo receptor recognition and has emerged as an important event in the regulation of liver physiology. Recent studies have shown that mitophagy may participate in the pathogenesis of various liver diseases, such as liver injury, liver steatosis/fatty liver disease, hepatocellular carcinoma, viral hepatitis, and hepatic fibrosis. This review summarizes the current knowledge on the molecular regulations and functions of mitophagy in liver physiology and the roles of mitophagy in the development of liver-related diseases. Furthermore, the therapeutic implications of targeting hepatic mitophagy to design a new strategy to cure liver diseases are discussed.
Keywords: autophagy; fibrosis; hepatitis; hepatocellular carcinoma; liver disease; liver injury; mitophagy; steatosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding: This research was funded by the National Health Research Institute (NHRI-EX103-10322SC, NHRI-EX104-10322SC, NHRI-EX105-10322SC, and NHRI-EX106-10322SC), Miaoli; the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST 102-2320-B-182-037-MY3, MOST 105-2628-B-182-001-MY3, and MOST108-2320-B-182-011), Taipei; and Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (CMRPD1C0211, CMRPD1D0021, CMRPD1D0022, CMRPD1D0023, CMRPD1G0281, CRRPD1F0031, CRRPD1F0032, CRRPD1F0033 and CMRPD1H0681), Taoyuan, Taiwan.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

