Soft Sensor Application in Identification of the Activated Sludge Bulking Considering the Technological and Economical Aspects of Smart Systems Functioning
- PMID: 32235669
- PMCID: PMC7180765
- DOI: 10.3390/s20071941
Soft Sensor Application in Identification of the Activated Sludge Bulking Considering the Technological and Economical Aspects of Smart Systems Functioning
Abstract
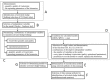
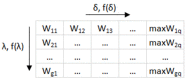
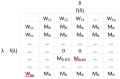
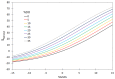
The paper presented the methodology for the construction of a soft sensor used for activated sludge bulking identification. Devising such solutions fits within the current trends and development of a smart system and infrastructure within smart cities. In order to optimize the selection of the data-mining method depending on the data collected within a wastewater treatment plant (WWTP), a number of methods were considered, including: artificial neural networks, support vector machines, random forests, boosted trees, and logistic regression. The analysis conducted sought the combinations of independent variables for which the devised soft sensor is characterized with high accuracy and at a relatively low cost of determination. With the measurement results pertaining to the quantity and quality of wastewater as well as the temperature in the activated sludge chambers, a good fit can be achieved with the boosted trees method. In order to simplify the selection of an optimal method for the identification of activated sludge bulking depending on the model requirements and the data collected within the WWTP, an original system of weight estimation was proposed, enabling a reduction in the number of independent variables in a model-quantity and quality of wastewater, operational parameters, and the cost of conducting measurements.
Keywords: activated sludge bulking.; classification model; data mining; smart systems and infrastructure; soft sensor; wastewater treatment plant.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Longo S., Mauricio-Iglesias M., Soares A., Campo P., Fatone F., Eusebi A.L., Akkersdijk E., Stefani L., Hospido A. ENERWATER—A standard method for assessing and improving the energy efficiency of wastewater treatment plants. Appl. Energy. 2019;242:897–910. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.03.130. - DOI
-
- Hollands R.G. Will the real smart city please stand up? City. 2008;12:303–320. doi: 10.1080/13604810802479126. - DOI
-
- Hashem I.A.T., Chang V., Anuar N.B., Adewole K., Yaqoob I., Gani A., Ahmed E., Chiroma H. The role of big data in smart city. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2016;36:748–758. doi: 10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2016.05.002. - DOI
-
- Visvizi A., Lytras M. It’s Not a Fad: Smart Cities and Smart Villages Research in European and Global Contexts. Sustainability. 2018;10:2727. doi: 10.3390/su10082727. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

