The resveratrol analogue, HS‑1793, enhances the effects of radiation therapy through the induction of anti‑tumor immunity in mammary tumor growth
- PMID: 32236622
- PMCID: PMC7170036
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2020.5017
The resveratrol analogue, HS‑1793, enhances the effects of radiation therapy through the induction of anti‑tumor immunity in mammary tumor growth
Abstract
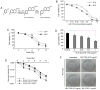
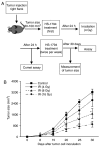
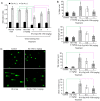
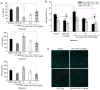
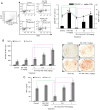
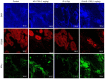
Radiotherapy can induce the infiltration of immune suppressive cells which are involved in promoting tumor progression and recurrence. A number of natural products with immunomodulating abilities have been gaining attention as complementary cancer treatments. This attention is partly due to therapeutic strategies which have proven to be ineffective as a result of tumor‑induced immunosuppressive cells found in the tumor microenvironment. The present study investigated whether HS‑1793, a resveratrol analogue, can enhance the antitumor effects by inhibiting lymphocyte damage and immune suppression by regulatory T cells (Tregs) and tumor‑associated macrophages (TAMs), during radiation therapy. FM3A cells were used to determine the role of HS‑1793 in the radiation‑induced tumor immunity of murine breast cancer. HS‑1793 treatment with radiation significantly increased lymphocyte proliferation with concanavalin A (Con A) stimulation and reduced the DNA damage of lymphocytes in irradiated tumor‑bearing mice. The administration of HS‑1793 also decreased the number of Tregs, and reduced interleukin (IL)‑10 and transforming growth factor (TGF)‑β secretion in irradiated tumor‑bearing mice. In addition, HS‑1793 treatment inhibited CD206+ TAM infiltration in tumor tissue when compared to the controls or irradiation alone. Mechanistically, HS‑1793 suppressed tumor growth via the activation of effector T cells in irradiated mice. On the whole, the findings of the present study reveal that HS‑1793 treatment improves the outcome of radiation therapy by enhancing antitumor immunity. Indeed, HS‑1793 appears to be a good therapeutic candidate for use in combination with radiotherapy in breast cancer.
Keywords: radiotherapy; HS‑1793; resveratrol analogue; regulatory T cells; tumor‑associated macrophages; antitumor immunity; breast cancer.
Figures

References
-
- Clarke M, Collins R, Darby S, Davies C, Elphinstone P, Evans V, Godwin J, Gray R, Hicks C, James S, et al. Effects of radio-therapy and of differences in the extent of surgery for early breast cancer on local recurrence and 15-year survival: An overview of the randomised trials. Lancet. 2005;366:2087–2106. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67887-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bartelink H, Horiot JC, Poortmans PM, Struikmans H, Van den Bogaert W, Fourquet A, Jager JJ, Hoogenraad WJ, Oei SB, Wárlám-Rodenhuis CC, et al. Impact of a higher radiation dose on local control and survival in breast-conserving therapy of early breast cancer: 10-Year results of the randomized boost versus no boost EORTC 22881-10882 trial. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:3259–3265. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.11.4991. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
