Reduced Apolipoprotein M and Adverse Outcomes Across the Spectrum of Human Heart Failure
- PMID: 32237898
- PMCID: PMC7200273
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.045323
Reduced Apolipoprotein M and Adverse Outcomes Across the Spectrum of Human Heart Failure
Abstract
Background: Apo (apolipoprotein) M mediates the physical interaction between high-density lipoprotein (HDL) particles and sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P). Apo M exerts anti-inflammatory and cardioprotective effects in animal models.
Methods: In a subset of PHFS (Penn Heart Failure Study) participants (n=297), we measured apo M by Enzyme-Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay (ELISA). We also measured total S1P by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and isolated HDL particles to test the association between apo M and HDL-associated S1P. We confirmed the relationship between apo M and outcomes using modified aptamer-based apo M measurements among 2170 adults in the PHFS and 2 independent cohorts: the Washington University Heart Failure Registry (n=173) and a subset of TOPCAT (Treatment of Preserved Cardiac Function Heart Failure With an Aldosterone Antagonist Trial; n=218). Last, we examined the relationship between apo M and ≈5000 other proteins (SomaScan assay) to identify biological pathways associated with apo M in heart failure.
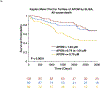
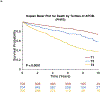
Results: In the PHFS, apo M was inversely associated with the risk of death (standardized hazard ratio, 0.56 [95% CI, 0.51-0.61]; P<0.0001) and the composite of death/ventricular assist device implantation/heart transplantation (standardized hazard ratio, 0.62 [95% CI, 0.58-0.67]; P<0.0001). This relationship was independent of HDL cholesterol or apo AI levels. Apo M remained associated with death (hazard ratio, 0.78 [95% CI, 0.69-0.88]; P<0.0001) and the composite of death/ventricular assist device/heart transplantation (hazard ratio, 0.85 [95% CI, 0.76-0.94]; P=0.001) in models that adjusted for multiple confounders. This association was present in both heart failure with reduced and preserved ejection fraction and was replicated in the Washington University cohort and a cohort with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction only (TOPCAT). The S1P and apo M content of isolated HDL particles strongly correlated (R=0.81, P<0.0001). The top canonical pathways associated with apo M were inflammation (negative association), the coagulation system (negative association), and liver X receptor/retinoid X receptor activation (positive association). The relationship with inflammation was validated with multiple inflammatory markers measured with independent assays.
Conclusions: Reduced circulating apo M is independently associated with adverse outcomes across the spectrum of human heart failure. Further research is needed to assess whether the apo M/S1P axis is a suitable therapeutic target in heart failure.
Keywords: apolipoproteins M; heart failure; lipoproteins, HDL; sphingosine-1-phosphate; survival.
Figures






References
-
- Christoffersen C, Nielsen LB, Axler O, Andersson A, Johnsen AH and Dahlback B. Isolation and characterization of human apolipoprotein M-containing lipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 2006;47:1833–1843. - PubMed
-
- Xu N and Dahlback B. A novel human apolipoprotein (apoM). J Biol Chem. 1999;274:31286–1290. - PubMed
-
- Elsoe S, Ahnstrom J, Christoffersen C, Hoofnagle AN, Plomgaard P, Heinecke JW, Binder CJ, Bjorkbacka H, Dahlback B and Nielsen LB. Apolipoprotein M binds oxidized phospholipids and increases the antioxidant effect of HDL. Atherosclerosis. 2012;221:91–97. - PubMed
-
- Christoffersen C, Jauhiainen M, Moser M, Porse B, Ehnholm C, Boesl M, Dahlback B and Nielsen LB. Effect of apolipoprotein M on high density lipoprotein metabolism and atherosclerosis in low density lipoprotein receptor knock-out mice. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:1839–1847. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U10 HL110338/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL107594/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL094307/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL102222/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007081/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL104106/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R61 HL146390/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 HL136730/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG058969/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL119962/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL138262/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL141232/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100026C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL121510/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

