Are COPD self-management mobile applications effective? A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 32238810
- PMCID: PMC7113264
- DOI: 10.1038/s41533-020-0167-1
Are COPD self-management mobile applications effective? A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
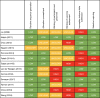
The burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) to patients and health services is steadily increasing. Self-management supported by mobile device applications could improve outcomes for people with COPD. Our aim was to synthesize evidence on the effectiveness of mobile health applications compared with usual care. A systematic review was conducted to identify randomized controlled trials. Outcomes of interest included exacerbations, physical function, and Quality of Life (QoL). Where possible, outcome data were pooled for meta-analyses. Of 1709 citations returned, 13 were eligible trials. Number of exacerbations, quality of life, physical function, dyspnea, physical activity, and self-efficacy were reported. Evidence for effectiveness was inconsistent between studies, and the pooled effect size for physical function and QoL was not significant. There was notable variation in outcome measures used across trials. Developing a standardized outcome-reporting framework for digital health interventions in COPD self-management may help standardize future research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organisation. The Global Burden of Disease. (2008) https://www.who.int/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/GBD_report_2004upda....
-
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease. Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. 2018 report (2018).
-
- Foundation, B. L. Estimating the Economic Burden Of Respiratory Illness in the UK blf Estimating the Economic Burden of Respiratory Illness in the UK, British Lung Foundation (2014).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

