Evaluation of Partial Oral Antibiotic Treatment for Persons Who Inject Drugs and Are Hospitalized With Invasive Infections
- PMID: 32239136
- PMCID: PMC7745005
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciaa365
Evaluation of Partial Oral Antibiotic Treatment for Persons Who Inject Drugs and Are Hospitalized With Invasive Infections
Abstract
Background: Persons who inject drugs (PWID) are at risk of invasive infections; however, hospitalizations to treat these infections are frequently complicated by against medical advice (AMA) discharges. This study compared outcomes among PWID who (1) completed a full course of inpatient intravenous (IV) antibiotics, (2) received a partial course of IV antibiotics but were not prescribed any antibiotics on AMA discharge, and (3) received a partial course of IV antibiotics and were prescribed oral antibiotics on AMA discharge.
Methods: A retrospective, cohort study of PWID aged ≥18 years admitted to a tertiary referral center between 01/2016 and 07/2019, who received an infectious diseases consultation for an invasive bacterial or fungal infection.
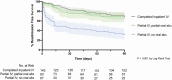
Results: 293 PWID were included in the study. 90-day all-cause readmission rates were highest among PWID who did not receive oral antibiotic therapy on AMA discharge (n = 46, 68.7%), compared with inpatient IV (n = 43, 31.5%) and partial oral (n = 27, 32.5%) antibiotics. In a multivariate analysis, 90-day readmission risk was higher among PWID who did not receive oral antibiotic therapy on AMA discharge (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 2.32; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.41-3.82) and not different among PWID prescribed oral antibiotic therapy on AMA discharge (aHR, .99; 95% CI, .62-1.62). Surgical source control (aHR, .57; 95% CI, .37-.87) and addiction medicine consultation (aHR, .57; 95% CI, .38-.86) were both associated with reduced readmissions.
Conclusions: Our single-center study suggests access to oral antibiotic therapy for PWID who cannot complete prolonged inpatient IV antibiotic courses is beneficial.
Keywords: endocarditis; opioid use disorder; osteomyelitis; substance abuse.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Baddour LM, Wilson WR, Bayer AS, et al. ; American Heart Association Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease of the Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, Council on Clinical Cardiology, Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia, and Stroke Council Infective endocarditis in adults: diagnosis, antimicrobial therapy, and management of complications: a scientific statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2015; 132:1435–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical