Effects of Dapagliflozin and Sitagliptin on Insulin Resistant and Body Fat Distribution in Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetic Patients
- PMID: 32240122
- PMCID: PMC7152738
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.921891
Effects of Dapagliflozin and Sitagliptin on Insulin Resistant and Body Fat Distribution in Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Abstract
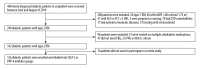
BACKGROUND The current study aimed to compare the effects of dapagliflozin and sitagliptin on insulin resistant and body fat distribution in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients. MATERIAL AND METHODS This study was an open-label, parallel controlled study. Patients were included if they were newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes (<6 months) and had been receiving dapagliflozin or sitagliptin for 12 weeks in combination with a stable dose of metformin in the last month. At baseline and 12 weeks, insulin resistant (homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance [HOMA-IR]), body fat distribution (waist/hip ratio), fasting blood glucose (FBG), glycated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), lipid profiles, and C-reactive protein (CRP) level were compared. RESULTS There were 59 patients receiving dapagliflozin and 67 patients receiving sitagliptin. There was no significant between-group difference in baseline characteristics. After 12 weeks of treatment, compared to the sitagliptin group, the FBG (6.4±0.5 versus 6.7±0.7 mmol/L), HbA1c (7.0±0.4 versus 7.2±0.5%), HOMA-IR (1.6±0.5 versus 1.8±0.6), triglyceride (1.6±0.4 versus 1.8±0.3 mmol/L), and CRP (3.1±0.7 versus 3.3±0.5 mg/L) were slightly lower in the dapagliflozin group. Within each group, compared to baseline, FBG (dapagliflozin [6.4±0.5 versus 7.8±0.7 mmol/L]; sitagliptin [6.7±0.7 versus 7.7±0.6 mmol/L]), HbA1c (dapagliflozin [7.0±0.4 versus 8.0±0.5%]; sitagliptin [7.2±0.5 versus 8.1%±0.6%]), HOMA-IR (dapagliflozin [1.6±0.5 versus 2.4±0.4]; sitagliptin [1.8±0.6 versus 2.5±0.4]), triglyceride (dapagliflozin [1.6±0.4 versus 2.2±0.5 mmol/L]; sitagliptin [1.8±0.3 versus 2.1±0.5 mmol/L]), and CRP (dapagliflozin [3.1±0.7 versus 6.2±1.1 mg/L]; sitagliptin [3.3±0.5 versus 6.1±1.0 mg/L]) were significantly decreased. CONCLUSIONS Dapagliflozin and sitagliptin had comparable effects on improving insulin resistant and blood glucose control, and these benefits may be associated with improvement of systemic inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of dapagliflozin versus sitagliptin on cardiometabolic risk factors in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: a prospective, randomized study (DIVERSITY-CVR).Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020 Jan 7;19(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12933-019-0977-z. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020. PMID: 31910850 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A randomized clinical trial of the efficacy and safety of sitagliptin compared with dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and mild renal insufficiency: The CompoSIT-R study.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018 Dec;20(12):2876-2884. doi: 10.1111/dom.13473. Epub 2018 Aug 16. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018. PMID: 30019498 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[Short-term intensive combined therapy with metformin, sagliptin and dapagliflozin for newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: efficacy, weight control and safety].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2019 Nov 30;39(11):1305-1311. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2019.11.07. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2019. PMID: 31852646 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
The efficacy of dapagliflozin combined with hypoglycaemic drugs in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.BMJ Open. 2014 Apr 7;4(4):e004619. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2013-004619. BMJ Open. 2014. PMID: 24710132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of three oral antidiabetic drugs on markers of β-cell function in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 25;8(10):e76713. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076713. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24204660 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of canagliflozin and metformin on insulin resistance and visceral adipose tissue in people with newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetes.BMC Endocr Disord. 2022 Feb 10;22(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s12902-022-00949-0. BMC Endocr Disord. 2022. PMID: 35144596 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview of the Cardioprotective Effects of Novel Antidiabetic Classes: Focus on Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Fibrosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 24;24(9):7789. doi: 10.3390/ijms24097789. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-inflammatory properties of antidiabetic drugs: A "promised land" in the COVID-19 era?J Diabetes Complications. 2020 Dec;34(12):107723. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2020.107723. Epub 2020 Aug 26. J Diabetes Complications. 2020. PMID: 32900588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Diabetic Atherosclerosis: The Role of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists, SGLT2 Inhibitors, and Nonsteroidal Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists in Vascular Protection and Disease Modulation.Biomedicines. 2025 Mar 17;13(3):728. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13030728. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40149704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retrospective Observational Study on Assessing Sitagliptin and Dapagliflozin as a Fixed-Dose Combination in the Indian Population With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: The SIDAXA Study.Cureus. 2024 May 21;16(5):e60815. doi: 10.7759/cureus.60815. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38910691 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sanchez EJ, Cefalu WT. Know diabetes by heart. Circulation. 2019;140(7):526–28. - PubMed
-
- Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Magliano DJ, Bennett PH. Diabetes mellitus statistics on prevalence and mortality: facts and fallacies. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016;12(10):616–22. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin EJ, Muntner P, Alonso A, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics – 2019 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2019;139(10):e56–528. - PubMed
-
- Nassif ME, Windsor SL, Tang F, et al. Dapagliflozin effects on biomarkers, symptoms, and functional status in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: The DEFINE-HF Trial. Circulation. 2019;140(18):1463–76. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous