Sterically stabilized recombined HDL composed of modified apolipoprotein A-I for efficient targeting toward glioma cells
- PMID: 32241173
- PMCID: PMC7170284
- DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2020.1745330
Sterically stabilized recombined HDL composed of modified apolipoprotein A-I for efficient targeting toward glioma cells
Abstract
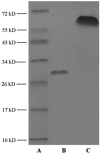
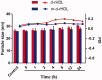
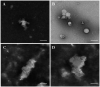
Reconstituted high density lipoprotein (rHDL) has been regarded as a promising brain-targeting vehicle for anti-glioma drugs under the mediation of apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I). However, some stability issues relating to drug leakage and consequent reduced targeting efficiency in the course of discoidal rHDL (d-rHDL) circulating in blood hinder its broad application. The objective of the study was to develop a novel stabilized d-rHDL by replacing cholesterol and apoA-I with mono-cholesterol glutarate (MCG) modified apoA-I (termed as mA) and to evaluate its allosteric behavior and glioma targeting. MCG was synthesized through esterifying the hydroxyl of cholesterol with glutaric anhydride and characterized by FI-IR and 1H NMR. d-rHDL assembled with mA (termed as m-d-rHDL) presented similar properties such as minute particle size and disk-like appearance resembling nascent HDL. Morphological transformation observation and in vitro release plots convinced that the modification of cholesterol could effectively inhibit the remolding of d-rHDL. The uptake of m-d-rHDL by LCAT-pretreated bEND.3 cells was significantly higher than that of d-rHDL, thereby serving as another proof for the capability of m-d-rHDL in enhancing targeting property. Besides, apoA-I anchoring into m-d-rHDL played a critical role in the endocytosis process into bEND.3 cells and C6 cells, which implied the possibility of traversing blood brain barrier and accumulating in the brain and glioma. These results suggested that the modification toward cholesterol to improve the stability of d-rHDL is advantageous, and that this obtained m-d-rHDL revealed great potential for realization of suppressing the remolding of d-rHDL in the brain-targeted treatment of glioma for drug delivery.
Keywords: BBB; LCAT; allosteric; cholesterol modification; glioma; rHDL.
Figures









References
-
- Asztalos BF, Schaefer EJ, Horvath KV, et al. (2007). Role of LCAT in HDL remodeling: investigation of LCAT deficiency states. J Lipid Res 48:592–9. - PubMed
-
- Bhuiyan MHU, Saidur R, Mostafizur RM, et al. (2015). Experimental investigation on surface tension of metal oxide–water nanofluids. Int Commun Heat Mass Transfer 65:82–8.
-
- Carlucci A, Cigliano L, Maresca B. (2012). LCAT cholesterol esterification is associated with the increase of ApoE/ApoA-I ratio during atherosclerosis progression in rabbit. J Physiol Biochem 68:541–53. - PubMed
-
- Chen R, Cohen AL, Colman H. (2016). Targeted therapeutics in patients with high-grade gliomas: past, present, and future. Curr Treat Options Oncol 17:42. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
