Vitamin D3 enhanced intestinal phosphate cotransporter genes in young and growing broilers
- PMID: 32241489
- PMCID: PMC7587629
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2019.11.038
Vitamin D3 enhanced intestinal phosphate cotransporter genes in young and growing broilers
Abstract
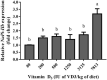
The influence of dietary vitamin D3 (VD3) levels on growth, bone performance, and duodenal type IIb sodium-dependent phosphate cotransporter (NaPi-IIb) genes in broiler chicken were studied. One-day-old male Ross308 broilers (n = 432) were allocated into 6 treatment groups with each group consisting of 6 cage pens. Each treatment group received diet containing different amounts of VD3 (80, 200, 500, 1,250, 3,125, or 7,813 IU per kg of diet) from a day-old to 31 D of age. Dietary available phosphorus and calcium were kept the same across all treatments in each phase. At 14 D, influence of VD3 on BW gain was found in the birds that received VD3 of 3,125 IU/kg and 200 IU/kg (P < 0.05). Toe ash and tibia ash linearly increased (P < 0.05) at 14 D with increase in dietary VD3. There was no significant influence of dietary VD3 on tibia breaking strength. In both phases, relative expression of duodenal NaPi-IIb linearly increased (P < 0.01) with increase in dietary VD3. At 14 D, highest expression of 3.2 folds was observed in birds treated with VD3 at 7,813 IU/kg of feed. At 31 D, birds that received VD3 levels of 3,125 and 7,813 IU/kg of feed showed 2.9 folds higher in NaPi-IIb expression compared with those fed lowest level of VD3 at 80 IU/kg of feed. When dietary calcium and phosphorus were maintained at the standard requirement, increase in dietary VD3 did not improve growth performance. For optimum growth and bone characteristics, dietary inclusion of VD3 at 500 IU/kg was adequate for both starter and grower broiler diets. Vitamin D3 enhanced the expression of NaPi-IIb at higher doses and thus improving the tibia ash content in high VD3 treatment groups. This study reported for the first time an increased in the expression of duodenal NaPi-IIb in 31-day-old broilers in response to high dietary VD3 levels.
Keywords: bone characteristics; broiler; gene expression; phosphate cotransporter; vitamin D(3).
Copyright © 2019. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Restriction of dietary non-phytate phosphorus on growth performance and expression of intestinal phosphate cotransporter genes in broilers.Poult Sci. 2019 Oct 1;98(10):4685-4693. doi: 10.3382/ps/pez171. Poult Sci. 2019. PMID: 30982064
-
Age, phosphorus, and 25-hydroxycholecalciferol regulate mRNA expression of vitamin D receptor and sodium-phosphate cotransporter in the small intestine of broiler chickens.Poult Sci. 2018 Apr 1;97(4):1199-1208. doi: 10.3382/ps/pex407. Poult Sci. 2018. PMID: 29325125
-
Dietary supplemental vitamin D3 enhances phosphorus absorption and utilisation by regulating gene expression of related phosphate transporters in the small intestine of broilers.Br J Nutr. 2019 Jan;121(1):9-21. doi: 10.1017/S0007114518002763. Epub 2018 Oct 29. Br J Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30370888
-
1α-Hydroxycholecalciferol improves the growth performance and up-regulates the mRNA expression of vitamin D receptor in the small intestine and kidney of broiler chickens.Poult Sci. 2018 Apr 1;97(4):1263-1270. doi: 10.3382/ps/pex423. Poult Sci. 2018. PMID: 29452375
-
Dietary vitamin D: growth, physiological and health consequences in broiler production.Anim Biotechnol. 2023 Nov;34(4):1635-1641. doi: 10.1080/10495398.2021.2013861. Epub 2021 Dec 19. Anim Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 34923931 Review.
Cited by
-
Intestinal segment and vitamin D3 concentration affect gene expression levels of calcium and phosphorus transporters in broiler chickens.J Anim Sci Technol. 2023 Mar;65(2):336-350. doi: 10.5187/jast.2022.e78. Epub 2023 Mar 31. J Anim Sci Technol. 2023. PMID: 37093912 Free PMC article.
-
Growth Performance and Gut Health of Cold-Stressed Broilers in Response to Supplementation with a Combination of Sodium Butyrate and Vitamin D3.Animals (Basel). 2025 Mar 17;15(6):861. doi: 10.3390/ani15060861. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40150390 Free PMC article.
-
Tibial adaptations to dietary 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 supplementation under two distinct vitamin regimens in young ducks.Poult Sci. 2025 Jun;104(6):105145. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105145. Epub 2025 Apr 7. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40245539 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of 1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol Glycoside Supplementation on the Growth, Intestinal Health, and Immunity of Broilers from Breeders Supplemented or Not with the Same Additive.Vet Sci. 2025 May 1;12(5):434. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12050434. Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40431526 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angel R., Saylor W.W., Dhandu A.S., Powers W., Applegate T.J. Effects of dietary phosphorus, phytase, and 25-hydroxycholecalciferol on performance of broiler chickens grown in floor pens. Poult. Sci. 2005;847:1031–1044. - PubMed
-
- Applegate T., Angel R., Classen H. Effect of dietary calcium, 25-hydroxycholecalciferol, or bird strain on small intestinal phytase activity in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2003;827:1140–1148. - PubMed
-
- Atencio A., Edwards H.M., Jr., Pesti G. Effects of vitamin D3 dietary supplementation of broiler breeder hens on the performance and bone abnormalities of the progeny 1. Poult. Sci. 2005;847:1058–1068. - PubMed
-
- Chen P., Huang Y., Bayir A., Wang C. Characterization of the isoforms of type IIb sodium-dependent phosphate cotransporter (Slc34a2) in yellow catfish, Pelteobagrus fulvidraco, and their vitamin D3-regulated expression under low-phosphate conditions. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2017;431:229–244. - PubMed
-
- Garcia A.R., Dale N.M. Foot ash as a means of Quantifying bone mineralization in chicks. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2006;151:103–109.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

