Complete Genome Sequence of Pantoea ananatis Strain NN08200, an Endophytic Bacterium Isolated from Sugarcane
- PMID: 32242244
- PMCID: PMC7334272
- DOI: 10.1007/s00284-020-01972-x
Complete Genome Sequence of Pantoea ananatis Strain NN08200, an Endophytic Bacterium Isolated from Sugarcane
Abstract
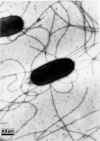
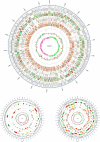
Stain NN08200 was isolated from the surface-sterilized stem of sugarcane grown in Guangxi province of China. The stain was Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, non-spore-forming bacteria. The complete genome SNP-based phylogenetic analysis indicate that NN08200 is a member of the genus Pantoea ananatis. Here, we summarize the features of strain NN08200 and describe its complete genome. The genome contains a chromosome and two plasmids, in total 5,176,640 nucleotides with 54.76% GC content. The chromosome genome contains 4598 protein-coding genes, and 135 ncRNA genes, including 22 rRNA genes, 78 tRNA genes and 35 sRNA genes, the plasmid 1 contains 149 protein-coding genes and the plasmid 2 contains 308 protein-coding genes. We identified 130 tandem repeats, 101 transposon genes, and 16 predicted genomic islands on the chromosome. We found an indole pyruvate decarboxylase encoding gene which involved in the biosynthesis of the plant hormone indole-3-acetic acid, it may explain the reason why NN08200 stain have growth-promoting effects on sugarcane. Considering the pathogenic potential and its versatility of the species of the genus Pantoea, the genome information of the strain NN08200 give us a chance to determine the genetic background of interactions between endophytic enterobacteria and plants.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Insights into the Potential Role of Plasmids in the Versatility of the Genus Pantoea.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Dec;66(12):3398-3414. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00960-3. Epub 2023 Nov 26. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38007817 Review.
-
Complete genome sequences of two Pantoea stewartii strains ATCC 8199 from maize and PSCN1 from sugarcane.BMC Genom Data. 2024 Oct 8;25(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s12863-024-01268-0. BMC Genom Data. 2024. PMID: 39379804 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the pathogenic function of Pantoea ananatis endogenous plasmid by an efficient and simple plasmid elimination strategy.Microbiol Res. 2021 May;246:126710. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2021.126710. Epub 2021 Jan 28. Microbiol Res. 2021. PMID: 33556709
-
Draft genome sequence of Pantoea ananatis B1-9, a nonpathogenic plant growth-promoting bacterium.J Bacteriol. 2012 Feb;194(3):729. doi: 10.1128/JB.06484-11. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22247529 Free PMC article.
-
Virulence mechanisms and host specificity of gall-forming Pantoea agglomerans.Trends Microbiol. 2007 Dec;15(12):538-45. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2007.10.009. Epub 2007 Nov 19. Trends Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 18024130 Review.
Cited by
-
Pantoea phytostimulans sp. nov., a novel strain with plant growth-promoting properties.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2025 Apr;75(4):006764. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.006764. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40279255 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the Potential Role of Plasmids in the Versatility of the Genus Pantoea.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Dec;66(12):3398-3414. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00960-3. Epub 2023 Nov 26. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38007817 Review.
-
Biosynthetic Mechanisms of Secondary Metabolites Promoted by the Interaction Between Endophytes and Plant Hosts.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jul 11;13:928967. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.928967. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35898919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterisation of Plant Growth-Promoting Endophytic Bacteria from Sugarcane and Their Antagonistic Activity against Fusarium moniliforme.Trop Life Sci Res. 2021 Sep;32(3):97-118. doi: 10.21315/tlsr2021.32.3.6. Epub 2021 Sep 30. Trop Life Sci Res. 2021. PMID: 35656370 Free PMC article.
-
Complete Genome Sequence of Pantoea stewartii RON18713 from Brazil Nut Tree Phyllosphere Reveals Genes Involved in Plant Growth Promotion.Microorganisms. 2023 Jun 30;11(7):1729. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11071729. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37512901 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Feng YJ, Shen DL, Dong XZ, et al. In vitro symplasmata formation in the rice diazotrophic endophyte Pantoea agglomerans YS19. Plant Soil. 2003;255(2):435–444. doi: 10.1023/A:1026079203474. - DOI
-
- Choi Q, Kim H, Lee Y, et al. First report of sheathrot of rice caused by Pantoea ananatis in Korea. Plant Pathol J. 2012;28(3):331. doi: 10.5423/PPJ.DR.08.2011.0150. - DOI
-
- Zhang J, Zhang CW, Yang J, et al. Insights into endophytic bacterial community structures of seeds among various Oryza sativa L. rice genotypes. J Plant Growth Regul. 2019;38(1):93–102. doi: 10.1007/s00344-018-9812-0. - DOI
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- 31101122/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 31660025/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2017GXNSFBA198118/Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Province
- 2016GXNSFBA380009/Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Province
- 2017JM37/Scientific Research and Technology Development Program of Guangxi
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

