Alternative approaches to treat bacterial infections: targeting quorum-sensing
- PMID: 32243194
- PMCID: PMC11032741
- DOI: 10.1080/14787210.2020.1750951
Alternative approaches to treat bacterial infections: targeting quorum-sensing
Abstract
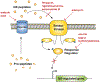
Introduction: The emergence of multi- and pan-drug-resistant bacteria represents a global crisis that calls for the development of alternative anti-infective strategies. These comprise anti-virulence approaches, which target pathogenicity without exerting a bacteriostatic or bactericidal effect and are claimed to reduce the development of resistance. Because in many pathogens, quorum-sensing (QS) systems control the expression of virulence factors, interference with QS, or quorum-quenching, is often proposed as a strategy with a broad anti-virulence effect.Areas covered: We discuss the role and regulatory targets of QS control in selected Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, focusing on those with clinical importance and QS control of virulence. We present the components of QS systems that form possible targets for the development of anti-virulence drugs and discuss recent research on quorum-quenching approaches to control bacterial infection.Expert opinion: While there has been extensive research on QS systems and quorum-quenching approaches, there is a paucity of in-vivo research using adequate animal models to substantiate applicability. In-vivo research on QS blockers needs to be intensified and optimized to use clinically relevant setups, in order to underscore that such drugs can be used effectively to overcome problems associated with the treatment of severe infections by antibiotic-resistant pathogens.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Quorum-sensing; Staphylococcus aureus; anti-virulence; biofilm; quorum-quenching.
Figures
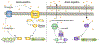

References
-
- WHO. No Time to Wait: Securing the future from drug-resistant infections. (Ed.^(Eds) (2019)
-
- Miller MB, Bassler BL. Quorum sensing in bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol, 55, 165–199 (2001). - PubMed
-
-
Passador L, Cook JM, Gambello MJ, Rust L, Iglewski BH. Expression of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence genes requires cell-to-cell communication. Science, 260(5111), 1127–1130 (1993).
** First report to show QS impact on virulence genes (in P. aeruginosa).
-
-
-
Recsei P, Kreiswirth B, O'Reilly M, Schlievert P, Gruss A, Novick RP. Regulation of exoprotein gene expression in Staphylococcus aureus by agr. Mol Gen Genet, 202(1), 58–61 (1986).
* First report on virulence regulation by the staphylococcal Agr locus (although the QS mechanism of the system was not yet known at that time.)
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
