The prognostic value of the C-reactive protein to albumin ratio in cancer: An updated meta-analysis
- PMID: 32243358
- PMCID: PMC7220550
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019165
The prognostic value of the C-reactive protein to albumin ratio in cancer: An updated meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have demonstrated that the C-reactive protein to albumin ratio (CAR) is correlated with the clinical outcomes of solid tumors. However, the available data have not been systematically evaluated. The objective of the present meta-analysis was to explore the prognostic value of the CAR in solid tumors.
Methods: Eligible studies were identified from the PubMed, EMBASE and Web of Science electronic databases. The clinical characteristics, disease -free survival (DFS) /progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were extracted from the eligible studies. The pooled hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals were calculated with STATA 12.0 software. We also performed subgroup, meta-regression and sensitivity analyses.
Results: In total, twenty-seven eligible studies including 10556 patients were enrolled in the present meta-analysis. The pooled HRs with 95% confidence intervals showed that the CAR was significantly associated with poor OS (HR = 1.95, 95% CI: 1.71-2.22) and DFS/PFS (HR = 1.82, 95% CI: 1.61-2.07) in patients with solid tumors. Although publication bias was found in the studies with regard to OS, a further trim and fill analysis revealed that the adjusted HR was 1.82 (95% CI: 1.69-1.96), which was close to the original HR. Subgroup analysis confirmed the CAR as a strong prognostic marker in patients with solid tumors, regardless of the tumor type, detection time, cut-off value, sample size and area.
Conclusion: Our meta-analysis indicated that a high CAR might be an unfavorable prognostic marker for OS and DFS/PFS in patients with solid tumors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures



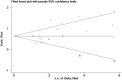


Similar articles
-
The prognostic value of serum amyloid A in solid tumors: a meta-analysis.Cancer Cell Int. 2019 Mar 20;19:62. doi: 10.1186/s12935-019-0783-4. eCollection 2019. Cancer Cell Int. 2019. PMID: 30930691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic role of pre-treatment C-reactive protein/albumin ratio in esophageal cancer: a meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2019 Nov 29;19(1):1161. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6373-y. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31783812 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of C-reactive protein (CRP) and albumin-based biomarker in patients with breast cancer receiving chemotherapy.PeerJ. 2025 May 21;13:e19319. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19319. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40416620 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic role of the pretreatment C-reactive protein/albumin ratio in gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Mar;99(10):e19362. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019362. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32150079 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of pretreatment C-reactive protein/albumin ratio in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A meta-analysis of published literature.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Jul;97(30):e11574. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011574. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30045284 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Preoperative High C-Reactive Protein to Albumin Ratio Predicts Short- and Long-Term Postoperative Outcomes in Elderly Gastric Cancer Patients.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jan 31;16(3):616. doi: 10.3390/cancers16030616. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38339365 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative Serum Hypersensitive-c-Reactive-Protein (Hs-CRP) to Albumin Ratio Predicts Survival in Patients with Luminal B Subtype Breast Cancer.Onco Targets Ther. 2021 Jul 9;14:4137-4148. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S320111. eCollection 2021. Onco Targets Ther. 2021. PMID: 34276217 Free PMC article.
-
Association of lung immune prognostic index with survival outcome in advanced thymic carcinoma patients treated with palliative intent chemotherapy.Thorac Cancer. 2022 Apr;13(7):1006-1013. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14349. Epub 2022 Feb 13. Thorac Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35156310 Free PMC article.
-
Pretreatment Nutritional Status in Combination with Inflammation Affects Chemotherapy Interruption in Women with Ovarian, Fallopian Tube, and Peritoneal Cancer.Nutrients. 2022 Dec 6;14(23):5183. doi: 10.3390/nu14235183. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36501212 Free PMC article.
-
Value of Platelet to Lymphocyte Ratio in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Various Stages.Iran J Otorhinolaryngol. 2024 May;36(3):467-473. doi: 10.22038/IJORL.2024.75070.3523. Iran J Otorhinolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 38745688 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

