Peritonsillar abscess may not always be a complication of acute tonsillitis: A prospective cohort study
- PMID: 32243441
- PMCID: PMC7122714
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228122
Peritonsillar abscess may not always be a complication of acute tonsillitis: A prospective cohort study
Abstract
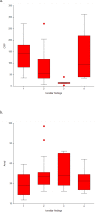
The present study aimed to specify diagnostics for peritonsillar abscesses (PTAs) and to clarify the role of minor salivary glands. This prospective cohort study included 112 patients with acute tonsillitis (AT) and PTA recruited at a tertiary hospital emergency department between February and October 2017. All patients completed a questionnaire concerning their current disease. Serum amylase (S-Amyl) and C-reactive protein (S-CRP) levels, tonsillar findings, and pus aspirate samples and throat cultures were analyzed. Eight of 58 PTA patients (13.8%) had no signs of tonsillar infection. The absence of tonsillar erythema and exudate was associated with low S-CRP (p<0.001) and older age (p<0.001). We also observed an inverse correlation between S-Amyl and S-CRP levels (AT, r = -0.519; PTA, r = -0.353). Therefore, we observed a group of PTA patients without signs of tonsillar infection who had significantly lower S-CRP levels than other PTA patients. These findings support that PTA may be caused by an etiology other than AT. Variations in the S-Amyl levels and a negative correlation between S-Amyl and S-CRP levels may indicate that minor salivary glands are involved in PTA development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

