Motion-robust, high-SNR liver fat quantification using a 2D sequential acquisition with a variable flip angle approach
- PMID: 32243665
- PMCID: PMC7366366
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.28263
Motion-robust, high-SNR liver fat quantification using a 2D sequential acquisition with a variable flip angle approach
Abstract
Purpose: Chemical shift encoded (CSE)-MRI enables quantification of proton-density fat fraction (PDFF) as a biomarker of liver fat content. However, conventional 3D Cartesian CSE-MRI methods require breath-holding. A motion-robust 2D Cartesian sequential method addresses this limitation but suffers from low SNR. In this work, a novel free breathing 2D Cartesian sequential CSE-MRI method using a variable flip angle approach with centric phase encoding (VFA-centric) is developed to achieve fat quantification with low bias, high SNR, and minimal blurring.
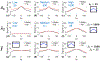
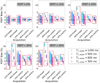
Methods: Numerical simulation was performed for variable flip angle schedule design and preliminary evaluation of VFA-centric method, along with several alternative flip angle designs. Phantom, adults (n = 8), and children (n = 27) were imaged at 3T. Multi-echo images were acquired and PDFF maps were estimated. PDFF standard deviation was used as a surrogate for SNR.
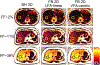
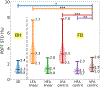
Results: In both simulation and phantom experiments, the VFA-centric method enabled higher SNR imaging with minimal bias and blurring artifacts. High correlation (slope = 1.00, intercept = 0.04, = 0.998) was observed in vivo between the proposed VFA-centric method obtained PDFF and reference PDFF (free breathing low-flip angle 2D sequential acquisition). Further, the proposed VFA-centric method (PDFF standard deviation = 1.5%) had a better SNR performance than the reference acquisition (PDFF standard deviation = 3.3%) with P < .001.
Conclusions: The proposed free breathing 2D Cartesian sequential CSE-MRI method with variable flip angle approach and centric-ordered phase encoding achieved motion robustness, low bias, high SNR compared to previous 2D sequential methods, and low blurring in liver fat quantification.
Keywords: 2D Cartesian; free breathing; high SNR; liver fat; low bias; low blurring artifact; variable flip angle.
© 2020 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures


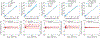
References
-
- Sanyal AJ, Banas C, Sargeant C, Luketic VA, Sterling RK, Stravitz RT, et al. Similarities and differences in outcomes of cirrhosis due to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and hepatitis C. Hepatology 2006;43(4):682–689. - PubMed
-
- Rubinstein E, Lavine JE, Schwimmer JB. Hepatic, cardiovascular, and endocrine outcomes of the histological subphenotypes of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease In: Seminars in liver disease, vol. 28 © Thieme Medical Publishers; 2008. p. 380–385. - PubMed
-
- Ekstedt M, Franzén LE, Mathiesen UL, Thorelius L, Holmqvist M, Bodemar G, et al. Long-term follow-up of patients with NAFLD and elevated liver enzymes. Hepatology 2006;44(4):865–873. - PubMed
-
- Puchner SB, Lu MT, Mayrhofer T, Liu T, Pursnani A, Ghoshhajra BB, et al. High-risk coronary plaque at coronary CT angiography is associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, independent of coronary plaque and stenosis burden: results from the ROMICAT II trial. Radiology 2014;274(3):693–701. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

