Smooth Muscle Cell Reprogramming in Aortic Aneurysms
- PMID: 32243809
- PMCID: PMC7182079
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2020.02.013
Smooth Muscle Cell Reprogramming in Aortic Aneurysms
Abstract
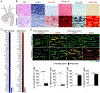
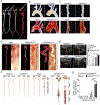
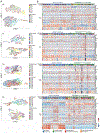
The etiology of aortic aneurysms is poorly understood, but it is associated with atherosclerosis, hypercholesterolemia, and abnormal transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) signaling in smooth muscle. Here, we investigated the interactions between these different factors in aortic aneurysm development and identified a key role for smooth muscle cell (SMC) reprogramming into a mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-like state. SMC-specific ablation of TGF-β signaling in Apoe-/- mice on a hypercholesterolemic diet led to development of aortic aneurysms exhibiting all the features of human disease, which was associated with transdifferentiation of a subset of contractile SMCs into an MSC-like intermediate state that generated osteoblasts, chondrocytes, adipocytes, and macrophages. This combination of medial SMC loss with marked increases in non-SMC aortic cell mass induced exuberant growth and dilation of the aorta, calcification and ossification of the aortic wall, and inflammation, resulting in aneurysm development.
Keywords: TGF-beta; aneurysm; aorta; artificial intelligence; atherosclerosis; cell fate; cell reprogramming; mesenchymal stem cell; scRNA-seq; smooth muscle cells.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests J.M.-L., S.G., and T.W.C. are employees of WuxiNextCode. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Baek S, Gleason RL, Rjagopal KR, and Humphrey JD (2007). Theory of small on large: Potential utility in computations of fluid–solid interactions in arteries. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 196, 3070–3078.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R35 HL135820/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD020142/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR070253/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL139796/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA212376/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL146723/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL134605/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI089992/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL134712/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL084312/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL135582/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL086418/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

