Variability in Genome Editing Outcomes: Challenges for Research Reproducibility and Clinical Safety
- PMID: 32243835
- PMCID: PMC7264426
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.03.015
Variability in Genome Editing Outcomes: Challenges for Research Reproducibility and Clinical Safety
Abstract
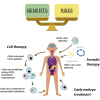
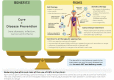
Genome editing tools have already revolutionized biomedical research and are also expected to have an important impact in the clinic. However, their extensive use in research has revealed much unpredictability, both off and on target, in the outcome of their application. We discuss the challenges associated with this unpredictability, both for research and in the clinic. For the former, an extensive validation of the model is essential. For the latter, potential unpredicted activity does not preclude the use of these tools but requires that molecular evidence to underpin the relevant risk:benefit evaluation is available. Safe and successful clinical application will also depend on the mode of delivery and the cellular context.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; clinical safety; functional genomics; gene delivery; gene therapy; medical research; research reproducibility.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Porteus M.H. A New Class of Medicines through DNA Editing. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019;380:947–959. - PubMed
-
- Mullard A. First in vivo CRISPR candidate enters the clinic. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019;18:656. - PubMed
-
- Ledford H. Quest to use CRISPR against disease gains ground. Nature. 2020;577:156. - PubMed
-
- Ledford H. CRISPR treatment inserted directly into the body for first time. Nature. 2020;579:185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

