KMT2D Deficiency Impairs Super-Enhancers to Confer a Glycolytic Vulnerability in Lung Cancer
- PMID: 32243837
- PMCID: PMC7178078
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.03.005
KMT2D Deficiency Impairs Super-Enhancers to Confer a Glycolytic Vulnerability in Lung Cancer
Abstract
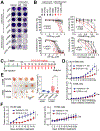
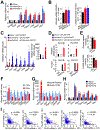
Epigenetic modifiers frequently harbor loss-of-function mutations in lung cancer, but their tumor-suppressive roles are poorly characterized. Histone methyltransferase KMT2D (a COMPASS-like enzyme, also called MLL4) is among the most highly inactivated epigenetic modifiers in lung cancer. Here, we show that lung-specific loss of Kmt2d promotes lung tumorigenesis in mice and upregulates pro-tumorigenic programs, including glycolysis. Pharmacological inhibition of glycolysis preferentially impedes tumorigenicity of human lung cancer cells bearing KMT2D-inactivating mutations. Mechanistically, Kmt2d loss widely impairs epigenomic signals for super-enhancers/enhancers, including the super-enhancer for the circadian rhythm repressor Per2. Loss of Kmt2d decreases expression of PER2, which regulates multiple glycolytic genes. These findings indicate that KMT2D is a lung tumor suppressor and that KMT2D deficiency confers a therapeutic vulnerability to glycolytic inhibitors.
Keywords: KMT2D; epigenetic modifier; glycolysis; histone methylation; histone methyltransferase; inhibitor; lung cancer; metabolism; super-enhancer; tumor suppressor.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Barski A, Cuddapah S, Cui K, Roh TY, Schones DE, Wang Z, Wei G, Chepelev I, and Zhao K (2007). High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell 129, 823–837. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

