Epigenomic and Transcriptomic Changes During Human RPE EMT in a Stem Cell Model of Epiretinal Membrane Pathogenesis and Prevention by Nicotinamide
- PMID: 32243845
- PMCID: PMC7160390
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2020.03.009
Epigenomic and Transcriptomic Changes During Human RPE EMT in a Stem Cell Model of Epiretinal Membrane Pathogenesis and Prevention by Nicotinamide
Abstract
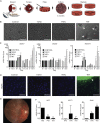
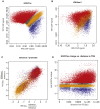
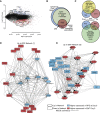
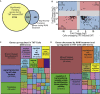
Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) is a biological process involved in tissue morphogenesis and disease that causes dramatic changes in cell morphology, migration, proliferation, and gene expression. The retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), which supports the neural retina, can undergo EMT, producing fibrous epiretinal membranes (ERMs) associated with vision-impairing clinical conditions, such as macular pucker and proliferative vitreoretinopathy (PVR). We found that co-treatment with TGF-β and TNF-α (TNT) accelerates EMT in adult human RPE stem cell-derived RPE cell cultures. We captured the global epigenomic and transcriptional changes elicited by TNT treatment of RPE and identified putative active enhancers associated with actively transcribed genes, including a set of upregulated transcription factors that are candidate regulators. We found that the vitamin B derivative nicotinamide downregulates these key transcriptional changes, and inhibits and partially reverses RPE EMT, revealing potential therapeutic routes to benefit patients with ERM, macular pucker and PVR.
Keywords: contractility; epigenetics; epithelial to mesenchymal transition; mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition; nicotinamide; proliferative vitreoretinopathy; retinal pigment epithelium; whole transcriptome.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Asato R., Yoshida S., Ogura A., Nakama T., Ishikawa K., Nakao S., Sassa Y., Enaida H., Oshima Y., Ikeo K. Comparison of gene expression profile of epiretinal membranes obtained from eyes with proliferative vitreoretinopathy to that of secondary epiretinal membranes. PLoS One. 2013;8:e54191. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blenkinsop T.A., Saini J.S., Maminishkis A., Bharti K., Wan Q., Banzon T., Lotfi M., Davis J., Singh D., Rizzolo L.J. Human adult retinal pigment epithelial stem cell-derived RPE monolayers exhibit key physiological characteristics of native tissue. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015;56:7085–7099. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blenkinsop T.A., Salero E., Stern J.H., Temple S. The culture and maintenance of functional retinal pigment epithelial monolayers from adult human eye. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013;945:45–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

