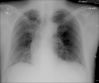
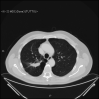
A Rapid Fatal Evolution of Coronavirus Disease-19 in a Patient With Advanced Lung Cancer With a Long-Time Response to Nivolumab
- PMID: 32243919
- PMCID: PMC7270552
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtho.2020.03.021
A Rapid Fatal Evolution of Coronavirus Disease-19 in a Patient With Advanced Lung Cancer With a Long-Time Response to Nivolumab
Figures
Comment in
-
Coronavirus Disease 2019 or Lung Cancer: A Differential Diagnostic Experience and Management Model From Wuhan.J Thorac Oncol. 2020 Aug;15(8):e141-e142. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2020.04.030. Epub 2020 May 7. J Thorac Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32387713 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Comment on
-
Cancer patients in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a nationwide analysis in China.Lancet Oncol. 2020 Mar;21(3):335-337. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30096-6. Epub 2020 Feb 14. Lancet Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32066541 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- WHO. Clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection (SARI) when COVID-19 disease is suspected: interim guidance version 1.2; 2020. https://apps.who.int/iris/rest/bitstreams/1272156/retrieve. Accessed March 13, 2020.
-
- Bersanelli M., Scala S., Affanni P. Immunological insights on influenza infection and vaccination during immune checkpoint blockade in cancer patients. Immunotherapy. 2020;12:105–110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical