LC-HRMS and Chemical Derivatization Strategies for the Structure Elucidation of Caribbean Ciguatoxins: Identification of C-CTX-3 and -4
- PMID: 32244322
- PMCID: PMC7230550
- DOI: 10.3390/md18040182
LC-HRMS and Chemical Derivatization Strategies for the Structure Elucidation of Caribbean Ciguatoxins: Identification of C-CTX-3 and -4
Abstract
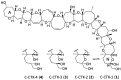
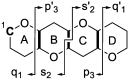
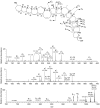
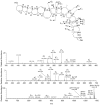
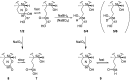
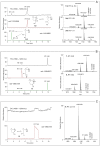
Ciguatera poisoning is linked to the ingestion of seafood that is contaminated with ciguatoxins (CTXs). The structural variability of these polyether toxins in nature remains poorly understood due to the low concentrations present even in highly toxic fish, which makes isolation and chemical characterization difficult. We studied the mass spectrometric fragmentation of Caribbean CTXs, i.e., the epimers C-CTX-1 and -2 (1 and 2), using a sensitive UHPLC-HRMS/MS approach in order to identify product ions of diagnostic value. We found that the fragmentation of the ladder-frame backbone follows a characteristic pattern and propose a generalized nomenclature for the ions formed. These data were applied to the structural characterization of a pair of so far poorly characterized isomers, C-CTX-3 and -4 (3 and 4), which we found to be reduced at C-56 relative to 1 and 2. Furthermore, we tested and applied reduction and oxidation reactions, monitored by LC-HRMS, in order to confirm the structures of 3 and 4. Reduction of 1 and 2 with NaBH4 afforded 3 and 4, thereby unambiguously confirming the identities of 3 and 4. In summary, this work provides a foundation for mass spectrometry-based characterization of new C-CTXs, including a suite of simple chemical reactions to assist the examination of structural modifications.
Keywords: Gambierdiscus; HRMS; LC–MS; Scomberomorus cavalla; Sphyraena barracuda; ciguatera; ciguatoxin; fragmentation pathways; ladder-frame molecule; polyether toxin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Friedman M.A., Fernandez M., Backer L.C., Dickey R.W., Bernstein J., Schrank K., Kibler S., Stephan W., Gribble M.O., Bienfang P., et al. An updated review of ciguatera fish poisoning: Clinical, epidemiological, environmental, and public health management. Mar. Drugs. 2017;15:72. doi: 10.3390/md15030072. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yasumoto T., Murata M. Marine Toxins. Chem. Rev. 1993;93:1897–1909. doi: 10.1021/cr00021a011. - DOI
-
- Kohli G.S., Campbell K., John U., Smith K.F., Fraga S., Rhodes L.L., Murray S.A. Role of modular polyketide synthases in the production of polyether ladder compounds in ciguatoxin-producing Gambierdiscus polynesiensis and G. excentricus (Dinophyceae) J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2017;64:691–706. doi: 10.1111/jeu.12405. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

