Lecithin-Based Dermal Drug Delivery for Anti-Pigmentation Maize Ceramide
- PMID: 32244349
- PMCID: PMC7180834
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25071595
Lecithin-Based Dermal Drug Delivery for Anti-Pigmentation Maize Ceramide
Abstract
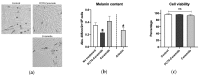
Ceramides have several well-known biological properties, including anti-pigmentation and anti-melanogenesis, which make them applicable for use in skincare products in cosmetics. However, the efficacy of ceramides is still limited. Dermal or transdermal drug delivery systems can enhance the anti-pigmentation properties of ceramides, although there is currently no systemic evaluation method for the efficacy of these systems. Here we prepared several types of lecithin-based emulsion of maize-derived glucosylceramide, determining PC70-ceramide (phosphatidylcholine-base) to be the safest and most effective anti-pigmentation agent using zebrafish larvae. We also demonstrated the efficacy of PC70 as a drug delivery system by showing that PC70-Nile Red (red fluorescence) promoted Nile Red accumulation in the larval bodies. In addition, PC70-ceramide suppressed melanin in mouse B16 melanoma cells compared to ceramide alone. In conclusion, we developed a lecithin-based dermal delivery method for ceramide using zebrafish larvae with implications for human clinical use.
Keywords: cone ceramide; in vivo imaging; zebrafish screening.
Conflict of interest statement
K.K., Y.F., A.H., and R.S. are employees of Tsuji Oil Mills Corporation, which is an oil company. The other authors declare no conflict of interest directly relevant to the content of this article.
Figures



References
-
- Hannun Y.A. The Sphingomyelin Cycle And The 2nd Messenger Function Of Ceramide. J. Biol. Chem. 1994;269:3125–3128. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

