The Influence of Preoperative Physical Activity on Postoperative Outcomes of Knee and Hip Arthroplasty Surgery in the Elderly: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 32244426
- PMCID: PMC7231073
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm9040969
The Influence of Preoperative Physical Activity on Postoperative Outcomes of Knee and Hip Arthroplasty Surgery in the Elderly: A Systematic Review
Abstract
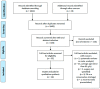
Total hip arthroplasty (THA) and total knee arthroplasty (TKA) represent two of the most common procedures in orthopedic surgery. The growing need to avoid physical impairment in elderly patients undergoing this kind of surgery puts the focus on the possibility to undertake a preoperative physical activity program to improve their fit and physical health at the time of surgery. A systematic review has been carried out with online databases including PubMed-Medline, Cochrane Central and Google Scholar. The aim was to retrieve available evidence concerning preoperative physical activity and exercise, before total knee or total hip arthroplasty in patients older than 65 years, and to clarify the role of this practice in improving postoperative outcomes. Results of the present systematic analysis showed that, for TKA, most of the studies demonstrated a comparable trend of postoperative improvement of Visual Analogue Scale (VAS), range of movement (ROM) and functional scores, and those of quality of life. There is insufficient evidence in the literature to draw final conclusions on the topic. Prehabilitation for patients undergoing TKA leads to shorter length of stay but not to an enhanced postoperative recovery. Concerning THA, although currently available data showed better outcomes in patients who underwent prehabilitation programs, there is a lack of robust evidence with appropriate methodology.
Keywords: arthroplasty; elderly; hip; knee; physical activity; prehabilitation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Withers T.M., Lister S., Sackley C., Clark A., Smith T.O. Is there a difference in physical activity levels in patients before and up to one year after unilateral total hip replacement? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Rehabil. 2017;31:639–650. doi: 10.1177/0269215516673884. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical