Activation of AMPK under Hypoxia: Many Roads Leading to Rome
- PMID: 32244507
- PMCID: PMC7177550
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21072428
Activation of AMPK under Hypoxia: Many Roads Leading to Rome
Abstract
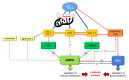
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is known as a pivotal cellular energy sensor, mediating the adaptation to low energy levels by deactivating anabolic processes and activating catabolic processes in order to restore the cellular ATP supply when the cellular AMP/ATP ratio is increased. Besides this well-known role, it has also been shown to exert protective effects under hypoxia. While an insufficient supply with oxygen might easily deplete cellular energy levels, i.e., ATP concentration, manifold other mechanisms have been suggested and are heavily disputed regarding the activation of AMPK under hypoxia independently from cellular AMP concentrations. However, an activation of AMPK preceding energy depletion could induce a timely adaptation reaction preventing more serious damage. A connection between AMPK and the master regulator of hypoxic adaptation via gene transcription, hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF), has also been taken into account, orchestrating their concerted protective action. This review will summarize the current knowledge on mechanisms of AMPK activation under hypoxia and its interrelationship with HIF.
Keywords: AMPK; CaMKK; FIH1; HIF; HIF-P4H; LKB1; [Ca2+i]; hypoxia; reactive oxygen species (ROS).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest
Figures
Similar articles
-
eNOS activation mediated by AMPK after stimulation of endothelial cells with histamine or thrombin is dependent on LKB1.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Feb;1813(2):322-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.12.001. Epub 2010 Dec 9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21145922
-
Interactions between HIF-1α and AMPK in the regulation of cellular hypoxia adaptation in chronic kidney disease.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015 Sep 1;309(5):F414-28. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00463.2014. Epub 2015 Jul 1. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26136559 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the prolyl-hydroxylase oxygen-sensing signal cascade leads to AMPK activation in cardiomyocytes.J Cell Mol Med. 2012 Sep;16(9):2049-59. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01500.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22128786 Free PMC article.
-
AMP-activated protein kinase in skeletal muscle: from structure and localization to its role as a master regulator of cellular metabolism.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008 Nov;65(23):3737-55. doi: 10.1007/s00018-008-8244-6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008. PMID: 18810325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AMPK-mTOR Signaling and Cellular Adaptations in Hypoxia.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 9;22(18):9765. doi: 10.3390/ijms22189765. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34575924 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Adaptive mechanisms in no flow vs. low flow ischemia in equine jejunum epithelium: Different paths to the same destination.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Sep 8;9:947482. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.947482. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36157182 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of hypoxia-induced Mucin 1 alters the proteomic composition of human osteoblast-produced extracellular matrix, leading to reduced osteogenic and angiogenic potential.J Cell Physiol. 2022 Feb;237(2):1440-1454. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30617. Epub 2021 Oct 22. J Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 34687046 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin as a regulator of apoptosis in leukaemia: molecular mechanism and therapeutic perspectives.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 14;14:1224151. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1224151. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37645444 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autophagy: A Friend or Foe in Allergic Asthma?Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 12;22(12):6314. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126314. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34204710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HIF-1-Independent Mechanisms Regulating Metabolic Adaptation in Hypoxic Cancer Cells.Cells. 2021 Sep 9;10(9):2371. doi: 10.3390/cells10092371. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34572020 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hawley S.A., Davison M., Woods A., Davies S.P., Beri R.K., Carling D., Hardie D.G. Characterization of the AMP-activated protein kinase kinase from rat liver and identification of threonine 172 as the major site at which it phosphorylates AMP-activated protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:27879–27887. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.44.27879. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

