Identification and Regulation of Interleukin-17 (IL-17) Family Ligands in the Teleost Fish European Sea Bass
- PMID: 32244562
- PMCID: PMC7178287
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21072439
Identification and Regulation of Interleukin-17 (IL-17) Family Ligands in the Teleost Fish European Sea Bass
Abstract
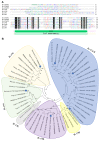
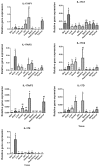
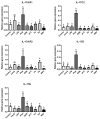
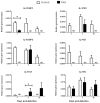
Interleukin-17 (IL-17) cytokine comprises a family of six ligands in mammals with proinflammatory functions, having an important role in autoimmune disorders and against bacterial, viral, and fungal pathogens. While IL-17A and IL-17F ligands are mainly produced by Th cells (Th17 cells), the rest of the ligands are expressed by other immune and non-immune cells and have different functions. The identification of IL-17 ligands in fish has revealed the presence of six members, counterparts to mammalian ones, and a teleost-specific form, the fish IL-17N. However, tissue distribution, the regulation of gene expression, and scarce bioactivity assays point to similar functions compared to mammalian ones, though this yet to be investigated and confirmed. Thus, we have identified seven IL-17 ligands in the teleost European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax), for the first time, corresponding to IL-17A/F1, IL-17A/F2, IL-17A/F3, IL-17C1, IL-17C2, IL-17D, and IL-17N, according to the predicted protein sequences and phylogenetic analysis. They are constitutively and widely transcribed in sea bass tissues, with some of them being mainly expressed in the thymus, brain or intestine. Upon in vitro stimulation of head-kidney leucocytes, the mRNA levels of all sea bass IL-17 ligands were up-regulated by phytohemagglutinin treatment, a well-known T cell mitogen, suggesting a major expression in T lymphocytes. By contrast, the infection of sea bass juveniles with nodavirus (NNV), a very pathogenic virus for this fish species, resulted in the up-regulation of the transcription of IL-17C1 in the head-kidney and of IL-17C1 and IL-17D in the brain, the target tissue for NNV replication. By contrast, NNV infection led to a down-regulated transcription of IL-17A/F1, IL-17A/F2, IL-17C1, IL-17C2, and IL-17D in the head-kidney and of IL-17A/F1 and IL-17A/F3 in the brain. The data are discussed accordingly with the IL-17 ligand expression and the immune response under the different situations tested.
Keywords: PAMPs; Th17 cells; fish; immunity; interleukin 17 (IL-17); nodavirus (NNV).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

