Novel Blotting Method for Mass Spectrometry Imaging of Metabolites in Strawberry Fruit by Desorption/Ionization Using Through Hole Alumina Membrane
- PMID: 32244711
- PMCID: PMC7230831
- DOI: 10.3390/foods9040408
Novel Blotting Method for Mass Spectrometry Imaging of Metabolites in Strawberry Fruit by Desorption/Ionization Using Through Hole Alumina Membrane
Abstract
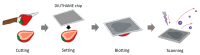
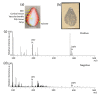
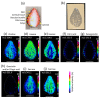
Mass spectrometry imaging (MSI) using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) is a powerful technique for visualizing metabolites in the strawberry fruit. During sample preparation for MALDI-MSI, sectioning of the samples is usually required. In general, MALDI-MSI analysis of strawberry fruits that are larger than a single glass slide is difficult because thin sections cannot be prepared. In this study, we attempted to visualize metabolites in large strawberry fruits by MSI, employing a blotting method that uses desorption ionization using a through-hole alumina membrane (DIUTHAME) chip. Large strawberry fruits were cut and a DIUTHAME chip was set on the cross-section to blot the metabolites. After drying the DIUTHAME chip, the metabolites were measured in positive and negative ion modes using a commercial MALDI-type mass spectrometer. Several peaks were detected in both the ion modes. Various metabolites related to food quality, such as sugars, organic acids, and anthocyanins, were detected and successfully visualized by blotting on a DIUTHAME chip in MSI. These results suggest that blotting using a DIUTHAME chip in MSI is useful for visualizing the metabolites present in the strawberry fruit.
Keywords: blotting; desorption ionization using through hole alumina membrane (DIUTHAME); mass spectrometry imaging; metabolites; strawberry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Matrix-Free High-Resolution Atmospheric-Pressure SALDI Mass Spectrometry Imaging of Biological Samples Using Nanostructured DIUTHAME Membranes.Metabolites. 2021 Sep 15;11(9):624. doi: 10.3390/metabo11090624. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 34564440 Free PMC article.
-
DIUTHAME enables matrix-free mass spectrometry imaging of frozen tissue sections.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2020 May 15;34(9):e8729. doi: 10.1002/rcm.8729. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2020. PMID: 31951673
-
Adhesive film applications help to prepare strawberry fruit sections for desorption electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry imaging.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2021 May 25;85(6):1341-1347. doi: 10.1093/bbb/zbab033. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33693621
-
Recent advances in matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation mass spectrometry imaging (MALDI-MSI) for in situ analysis of endogenous molecules in plants.Phytochem Anal. 2018 Jul;29(4):351-364. doi: 10.1002/pca.2759. Epub 2018 Apr 17. Phytochem Anal. 2018. PMID: 29667236 Review.
-
Promising mass spectrometry imaging: exploring microscale insights in food.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Jan 16:1-32. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2025.2451189. Online ahead of print. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39817602 Review.
Cited by
-
Localization of Flavan-3-ol Species in Peanut Testa by Mass Spectrometry Imaging.Molecules. 2020 May 20;25(10):2373. doi: 10.3390/molecules25102373. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32443878 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging applications of metabolomics in food science and future trends.Food Chem X. 2022 Nov 9;16:100500. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2022.100500. eCollection 2022 Dec 30. Food Chem X. 2022. PMID: 36519105 Free PMC article.
-
Spatiotemporal Visualization of Insecticides and Fungicides within Fruits and Vegetables Using Gold Nanoparticle-Immersed Paper Imprinting Mass Spectrometry Imaging.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 May 18;11(5):1327. doi: 10.3390/nano11051327. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34069856 Free PMC article.
-
MALDI MS Imaging of Cucumbers.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2688:63-69. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3319-9_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37410284
-
Matrix-Free High-Resolution Atmospheric-Pressure SALDI Mass Spectrometry Imaging of Biological Samples Using Nanostructured DIUTHAME Membranes.Metabolites. 2021 Sep 15;11(9):624. doi: 10.3390/metabo11090624. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 34564440 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

