Master Regulator Analysis of the SARS-CoV-2/Human Interactome
- PMID: 32244779
- PMCID: PMC7230814
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm9040982
Master Regulator Analysis of the SARS-CoV-2/Human Interactome
Abstract
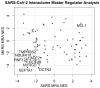
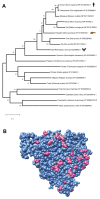
The recent epidemic outbreak of a novel human coronavirus called SARS-CoV-2 causing the respiratory tract disease COVID-19 has reached worldwide resonance and a global effort is being undertaken to characterize the molecular features and evolutionary origins of this virus. In this paper, we set out to shed light on the SARS-CoV-2/host receptor recognition, a crucial factor for successful virus infection. Based on the current knowledge of the interactome between SARS-CoV-2 and host cell proteins, we performed Master Regulator Analysis to detect which parts of the human interactome are most affected by the infection. We detected, amongst others, affected apoptotic and mitochondrial mechanisms, and a downregulation of the ACE2 protein receptor, notions that can be used to develop specific therapies against this new virus.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; bioinformatics; coronavirus; gene network analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Zeng Z.-Q., Chen D.-H., Tan W.-P., Qiu S.-Y., Xu D., Liang H.-X., Chen M.-X., Li X., Lin Z.-S., Liu W.-K., et al. Epidemiology and clinical characteristics of human coronaviruses OC43, 229E, NL63, and HKU1: A study of hospitalized children with acute respiratory tract infection in Guangzhou, China. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018;37:363–369. doi: 10.1007/s10096-017-3144-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhong N., Zheng B., Li Y., Poon L., Xie Z., Chan K., Li P., Tan S., Chang Q., Xie J., et al. Epidemiology and cause of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) in Guangdong, People’s Republic of China, in February, 2003. Lancet. 2003;362:1353–1358. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)14630-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

