Aquatic Plants, Landoltia punctata, and Azolla filiculoides as Bio-Converters of Wastewater to Biofuel
- PMID: 32244834
- PMCID: PMC7238415
- DOI: 10.3390/plants9040437
Aquatic Plants, Landoltia punctata, and Azolla filiculoides as Bio-Converters of Wastewater to Biofuel
Abstract
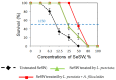
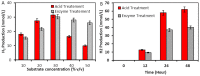
The aquatic plants, Azolla filiculoides, and Landoltia punctate, were used as complementing phytoremediators of wastewater containing high levels of phosphate, which simulates the effluents from textile, dyeing, and laundry detergent industries. Their complementarities are based on differences in capacities to uptake nitrogen and phosphate components from wastewater. Sequential treatment by L. punctata followed by A. filiculoides led to complete removal of NH4, NO3, and up to 93% reduction of PO4. In experiments where L. punctata treatment was followed by fresh L. punctata, PO4 concentration was reduced by 65%. The toxicity of wastewater assessed by shrimps, Paratya australiensis, showed a four-fold reduction of their mortality (LC50 value) after treatment. Collected dry biomass was used as an alternative carbon source for heterotrophic marine protists, thraustochytrids, which produced up to 35% dry weight of lipids rich in palmitic acid (50% of total fatty acids), the key fatty acid for biodiesel production. The fermentation of treated L. punctata biomass by Enterobacter cloacae yielded up to 2.14 mol H2/mole of reduced sugar, which is comparable with leading terrestrial feedstocks. A. filiculoides and L. punctata can be used as a new generation of feedstock, which can treat different types of wastewater and represent renewable and sustainable feedstock for bioenergy production.
Keywords: duckweed; hydrogen; phytoremediation; wastewater treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Marmiroli N., Marmiroli M., Maestri E. Phytoremediation and Phytotechnologies A Review for the Present and the Future. Soil Water Pollution. Monit. Protect. Remediat. 2006;69:403–416.
-
- Dushenkov S. Trends in phytoremediation of radionuclides. Plant Soil. 2003;249:167–175. doi: 10.1023/A:1022527207359. - DOI
-
- Miranda A.F., Muradov N., Gujar A., Stevenson T., Nugegoda D., Ball A.S., Mouradov A. Application of Aquatic plants for the treatment of selenium-rich mining wastewater and production of renewable fuels and petrochemicals. J. Sustain. Bioenergy Syst. 2014;4:97–112. doi: 10.4236/jsbs.2014.41010. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

