Dendritic Macrosurfactant Assembly for Physical Functionalization of HIPE-Templated Polymers
- PMID: 32244838
- PMCID: PMC7240670
- DOI: 10.3390/polym12040779
Dendritic Macrosurfactant Assembly for Physical Functionalization of HIPE-Templated Polymers
Abstract
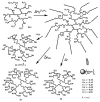
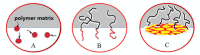
High-internal-phase emulsion-templated macroporous polymers (polyHIPEs) have attracted much interest, but their surface functionalization remains a primary concern. Thus, competitive surface functionalization via physical self-assembly of macrosurfactants was reviewed. Dendritic and diblock-copolymer macrosurfactants were tested, and the former appeared to be more topologically competitive in terms of solubility, viscosity, and versatility. In particular, hyperbranched polyethyleneimine (PEI) was transformed into dendritic PEI macrosurfactants through click-like N-alkylation with epoxy compounds. Free-standing PEI macrosurfactants were used as molecular nanocapsules for charge-selective guest encapsulation and robustly dictated the surface of a macroporous polymer through the HIPE technique, in which the macroporous polymer could act as a well-recoverable adsorbent. Metal nanoparticle-loaded PEI macrosurfactants could similarly lead to polyHIPE, whose surface was dictated by its catalytic component. Unlike conventional Pickering stabilizer, PEI macrosurfactant-based metal nanocomposite resulted in open-cellular polyHIPE, rendering the catalytic sites well accessible. The active amino groups on the polyHIPE could also be transformed into functional groups of aminopolycarboxylic acids, which could efficiently eliminate trace and heavy metal species in water.
Keywords: adsorption; dendritic macrosurfactant; functional surface; polyethyleneimine; porous organic polymer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Emulsion-Templated Porous Polymers for Efficient Dye Removal.ACS Omega. 2022 Apr 29;7(18):16127-16140. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c01472. eCollection 2022 May 10. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 35571856 Free PMC article.
-
Dendritic Amphiphile Mediated One-Pot Preparation of 3D Pt Nanoparticles-Decorated PolyHIPE as a Durable and Well-Recyclable Catalyst.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015 Sep 23;7(37):20885-92. doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b06283. Epub 2015 Sep 10. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015. PMID: 26327523
-
Pickering polymerized high internal phase emulsions: Fundamentals to advanced applications.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2025 Feb;336:103375. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2024.103375. Epub 2024 Dec 7. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2025. PMID: 39667091 Review.
-
Control of Uniform and Interconnected Macroporous Structure in PolyHIPE for Enhanced CO2 Adsorption/Desorption Kinetics.Environ Sci Technol. 2016 Jul 19;50(14):7879-88. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.6b00579. Epub 2016 Jun 30. Environ Sci Technol. 2016. PMID: 27322734
-
Porous Polymers from High Internal Phase Emulsions as Scaffolds for Biological Applications.Polymers (Basel). 2021 May 28;13(11):1786. doi: 10.3390/polym13111786. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34071683 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Feng Y.Y., Zhang X.X., Jin M., Wan D.C. Dendritic Macrosurfactant-Decorated PolyHIPE as a Highly Efficient and Well Recyclable Scavenger of Micropollutants in Water: Topological Effect. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2017;55:1294–1302. doi: 10.1002/pola.28455. - DOI
-
- Ye Y.L., Wan D.C., Du J., Jin M., Pu H.T. Dendritic Macrosurfactant Mediated Porous Monolith for Eliminating Organic Micropollutants from Water. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2015;3:6297–6300. doi: 10.1039/C4TA07097F. - DOI
-
- Ye Y.L., Jin M., Wan D.C. One-Pot to Porous Monolith-Supported Gold Nanoparticles as a Well Recyclable Catalyst. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2015;3:13519–13525. doi: 10.1039/C5TA02925B. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

