Availability of Authorizations from EMA and FDA for Age-Appropriate Medicines Contained in the WHO Essential Medicines List for Children 2019
- PMID: 32244848
- PMCID: PMC7238124
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12040316
Availability of Authorizations from EMA and FDA for Age-Appropriate Medicines Contained in the WHO Essential Medicines List for Children 2019
Abstract
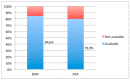
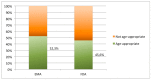
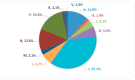
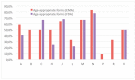
Lack of age-appropriate commercially drug products availability is a common problem in pediatric therapeutics; this population needs improved and safer drug delivery. In addition, biopharmaceutic aspects, dosage requirements, and swallowing abilities demand pediatric forms different to adult formulations. The objective of this study was to evaluate the authorization availability from United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European Medicines Agency (EMA) of oral essential medicines for children and analyze its age-appropriateness for oral administration in children. All oral drugs from 7th List of Essential Medicines for Children by World Health Organization (WHO) were selected. Availability of commercial drug products was collected from OrangeBook, Spanish drug product catalogue, British electronic Medicines Compendium, and the International Vademecum. Tablets, effervescent tablets, and capsules were considered as not age-appropriate forms. Liquid forms, powder for oral suspension, mini tablets, granules, and soluble films were considered as age-appropriate forms due to their flexibility. More than 80% of the studied drugs possess a commercial authorization in oral forms in both EMA and FDA. Nevertheless, around 50% of these formulations are not age-appropriate for most pediatric groups. This study shows the lack of age-appropriate medicines for children. More efforts are needed to improve development and approval of pediatric medicines.
Keywords: age appropriate; commercial availability; pediatrics; pharmaceutical preparations; regulatory; safety.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

