A Novel Hydraulic Actuation System Utilizing Magnetorheological Fluids for Single-Port Laparoscopic Surgery Applications
- PMID: 32244849
- PMCID: PMC7143166
- DOI: 10.3390/ma13061380
A Novel Hydraulic Actuation System Utilizing Magnetorheological Fluids for Single-Port Laparoscopic Surgery Applications
Abstract
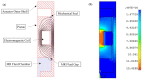
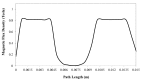
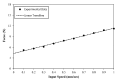
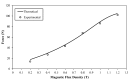
Single-port laparoscopic surgery (SLS), which utilizes one major incision, can deliver favorable cosmetic outcomes with fewer patient hospitalization stays and less postoperative pain. However, current SLS instruments, which are rigid and slender, have been suffering from several drawbacks, including their inability to provide the optimum articulation required to complete certain SLS tasks. This paper reports on the development of a lightweight smart hydraulic actuation system that is proposed to be embedded at selected joints along current SLS instruments, in order to enhance their adaptability with a higher level of stiffness and degrees-of-freedom. The developed smart actuation system utilizes both conventional hydraulic and magnetorheological (MR) fluid actuation technologies. Electromagnetic finite element analyses were conducted to design the electromagnetic circuit of the smart actuator. A prototype of the developed actuation system was manufactured, and its performance was assessed using a dedicated experimental arrangement, which was found to agree well with the results obtained using a Bingham plastic theoretical model. Finally, the present design of the developed smart actuation system permits an angulation of about 90° and a maximum force output in excess of 100 N, generated under a magnetic excitation of about 1.2 Tesla, which should be sufficient to resist torques of up to 500 mNm.
Keywords: magnetic-responsive materials; magnetorheological fluids; single-port laparoscopic surgery (SLS); smart hydraulic actuator; smart material actuator; smart materials.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
High-performance magneto-rheological clutches for direct-drive actuation: Design and development.J Intell Mater Syst Struct. 2021 Dec;32(20):2582-2600. doi: 10.1177/1045389X211006902. Epub 2021 Apr 16. J Intell Mater Syst Struct. 2021. PMID: 34764629 Free PMC article.
-
Highly-Integrated Hydraulic Smart Actuators and Smart Manifolds for High-Bandwidth Force Control.Front Robot AI. 2018 Jun 14;5:51. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2018.00051. eCollection 2018. Front Robot AI. 2018. PMID: 33659276 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental assessment of a linear actuator driven by magnetorheological clutches for automotive active suspensions.J Intell Mater Syst Struct. 2021 May;32(9):955-970. doi: 10.1177/1045389X21991237. Epub 2021 Feb 11. J Intell Mater Syst Struct. 2021. PMID: 34040332 Free PMC article.
-
Sensors and Sensing Devices Utilizing Electrorheological Fluids and Magnetorheological Materials-A Review.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Apr 29;24(9):2842. doi: 10.3390/s24092842. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38732948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Searching for a Stable High-Performance Magnetorheological Suspension.Adv Mater. 2018 Oct;30(42):e1704769. doi: 10.1002/adma.201704769. Epub 2018 Aug 27. Adv Mater. 2018. PMID: 30151957 Review.
References
-
- Miernik A., Schoenthaler M., Lilienthal K., Frankenschmidt A., Karcz W., Kuesters S. Pre-bent instruments used in single-port laparoscopic surgery versus conventional laparoscopic surgery: Comparative study of performance in a dry lab. Surg. Endosc. 2012;26:1924–1930. doi: 10.1007/s00464-011-2129-8. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

