Influence of Maternal Milk on the Neonatal Intestinal Microbiome
- PMID: 32244880
- PMCID: PMC7146310
- DOI: 10.3390/nu12030823
Influence of Maternal Milk on the Neonatal Intestinal Microbiome
Abstract
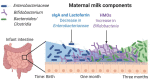
The intestinal microbiome plays an important role in maintaining health throughout life. The microbiota develops progressively after birth and is influenced by many factors, including the mode of delivery, antibiotics, and diet. Maternal milk is critically important to the development of the neonatal intestinal microbiota. Different bioactive components of milk, such as human milk oligosaccharides, lactoferrin, and secretory immunoglobulins, modify the composition of the neonatal microbiota. In this article, we review the role of each of these maternal milk-derived bioactive factors on the microbiota and how this modulation of intestinal bacteria shapes health, and disease.
Keywords: breast milk; human milk oligosaccharides; lactoferrin; maternal milk; neonatal microbiome; secretory IgA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors, K.P.G. and T.W.H., share a patent on a methodology to determine the specificity of antibodies from maternal milk samples.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

