Cross-Cultural Variation in BMI, Sedentary Behavior, and Physical Activity in International School Girls Residing in Saudi Arabia
- PMID: 32244890
- PMCID: PMC7142904
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17062057
Cross-Cultural Variation in BMI, Sedentary Behavior, and Physical Activity in International School Girls Residing in Saudi Arabia
Abstract
Background: The current study was done to assess the cross-cultural difference in physical activity and sedentary behavior among girls from culturally, environmentally, and geographically diverse countries residing in Saudi Arabia.
Methods: This was a comparative cross-sectional study conducted among expatriate girls (N = 275), aged 9-16 years. Participants were from India (n = 65), Pakistan (n = 88), Egypt (n = 50), Sudan (n = 49), and other nationals (n = 23). They were randomly selected from different schools in Riyadh and their Body Mass Index (BMI) and screen time was assessed. Physical activity (PA) and leisure-time activity was assessed using Physical Activity Questionnaire for Older Children (PAQ-C) and the Godin-Shephard Leisure-Time Exercise Questionnaire (GSLTPAQ) respectively.
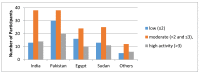
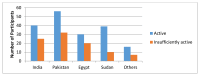
Results: Out of 275, 65.8% were active and 34.2% were insufficiently active as per the GSLTPAQ, and half of them were moderately active and only 22.2% were extremely active as per PAQ-C. No statistical significant differences in their BMI status, screen time, or the levels of PA among expatriate girls.
Conclusions: This study shows that the expatriate female school children in Saudi Arabia demonstrated a similar pattern in their BMI, sedentary time spent, and PA levels.
Keywords: body mass index; cross cultural; expatriate school children; physical inactivity; school girls.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Associations among Body Mass Index, sedentary behavior, physical activity, and academic performance in schoolchildren.J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2020 Dec;60(12):1551-1557. doi: 10.23736/S0022-4707.20.10482-1. Epub 2020 Apr 27. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2020. PMID: 32343080
-
Differences among Saudi and Expatriate Students: Body Composition Indices, Sitting Time Associated with Media Use and Physical Activity Pattern.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Jan 29;17(3):832. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17030832. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32013115 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of individual and family factors on physical activity among Saudi girls: a cross-sectional study.Ann Saudi Med. 2019 Jan-Feb;39(1):13-21. doi: 10.5144/0256-4947.2019.13. Ann Saudi Med. 2019. PMID: 30712046 Free PMC article.
-
Scoping Review of Population-Based Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior in Saudi Arabia.J Phys Act Health. 2023 Apr 25;20(6):471-486. doi: 10.1123/jpah.2022-0537. Print 2023 Jun 1. J Phys Act Health. 2023. PMID: 37185448
-
Physical inactivity in Saudi Arabia revisited: A systematic review of inactivity prevalence and perceived barriers to active living.Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2018 Nov-Dec;12(6):50-64. Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2018. PMID: 30534044 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Full-Day Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour Levels of Typically Developing Children and Adolescents in the Middle East: A Systematic Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Oct 19;20(20):6940. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20206940. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37887678 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Environmental Quality of Life in Physical Activity Status of Individuals with and without Physical Disabilities in Saudi Arabia.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Apr 1;19(7):4228. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19074228. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35409909 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring parents' perceptions and experiences of childhood obesity and management in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia: an interpretive qualitative study.BMC Public Health. 2024 Dec 18;24(1):3452. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-21014-6. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39696165 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Childhood Obesity Among Children and Adolescents in Saudi Arabia: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2024 Sep 24;16(9):e70135. doi: 10.7759/cureus.70135. eCollection 2024 Sep. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39463548 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Al-Asiri Z.A., Shaheen A.A.M. Body Mass Index and Health Related Physical Fitness in Saudi Girls and Adolescents Aged 8–15 Years. Open J. Ther. Rehabil. 2015;3:116–125. doi: 10.4236/ojtr.2015.34016. - DOI
-
- Abalkhail B. Overweight and obesity among Saudi Arabian children and adolescents between 1994 and 2000. East. Mediterr. Health J. 2004:8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical