Attenuation of Hyperoxic Lung Injury in Newborn Thioredoxin-1-Overexpressing Mice through the Suppression of Proinflammatory Cytokine mRNA Expression
- PMID: 32244938
- PMCID: PMC7148529
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines8030066
Attenuation of Hyperoxic Lung Injury in Newborn Thioredoxin-1-Overexpressing Mice through the Suppression of Proinflammatory Cytokine mRNA Expression
Abstract
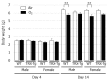
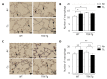
The role of thioredoxin-1 (TRX), a small redox-active protein with antioxidant effects, during hyperoxic lung injury in newborns remains undetermined. We investigated TRX impact on hyperoxic lung injury in newborn TRX transgenic (TRX-Tg) and wildtype (WT) mice exposed to 21% or 95% O2 for four days, after which some mice were allowed to recover in room air for up to 14 days. Lung morphology was assessed by hematoxylin/eosin and elastin staining, as well as immunostaining for macrophages. The gene expression levels of proinflammatory cytokines were evaluated using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. During recovery from hyperoxia, TRX-Tg mice exhibited an improved mean linear intercept length and increased number of secondary septa in lungs compared with the WT mice. Neonatal hyperoxia enhanced the mRNA expression levels of proinflammatory cytokines in the lungs of both TRX-Tg and WT mice. However, interleukin-6, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, and chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 2 mRNA expression levels were reduced in the lungs of TRX-Tg mice compared with the WT mice during recovery from hyperoxia. Furthermore, TRX-Tg mice exhibited reduced macrophage infiltration in lungs during recovery. These results suggest that in newborn mice TRX ameliorates hyperoxic lung injury during recovery likely through the suppression of proinflammatory cytokines.
Keywords: antioxidant effects; hyperoxic lung injury; newborn mice; proinflammatory cytokine gene expression; thioredoxin-1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest, or nonfinancial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Thioredoxin-1 Ameliorates Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy in Newborn Mice through Modulation of Proinflammatory and Angiogenic Factors.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Apr 30;11(5):899. doi: 10.3390/antiox11050899. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35624763 Free PMC article.
-
Thioredoxin-deficient mice, a novel phenotype sensitive to ambient air and hypersensitive to hyperoxia-induced lung injury.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015 Mar 1;308(5):L429-42. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00285.2014. Epub 2014 Dec 24. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25539854 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic ablation of Bach1 gene enhances recovery from hyperoxic lung injury in newborn mice via transient upregulation of inflammatory genes.Pediatr Res. 2017 Jun;81(6):926-931. doi: 10.1038/pr.2017.17. Epub 2017 Jan 18. Pediatr Res. 2017. PMID: 28099425
-
Thioredoxin-1 protects against hyperoxia-induced apoptosis in cells of the alveolar walls.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2007;20(6):650-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2006.07.004. Epub 2006 Sep 1. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2007. PMID: 17045827
-
The thioredoxin system in neonatal lung disease.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014 Nov 1;21(13):1916-25. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5782. Epub 2014 Mar 13. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014. PMID: 24328910 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Post-translational modifications and bronchopulmonary dysplasia.Front Pediatr. 2025 Jan 3;12:1426030. doi: 10.3389/fped.2024.1426030. eCollection 2024. Front Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 39830627 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The serum thioredoxin-1 levels are not associated with bronchopulmonary dysplasia and retinopathy of prematurity.Pediatr Res. 2024 Oct;96(5):1275-1282. doi: 10.1038/s41390-024-03078-7. Epub 2024 Feb 16. Pediatr Res. 2024. PMID: 38365875 Free PMC article.
-
Thioredoxin-1 Ameliorates Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy in Newborn Mice through Modulation of Proinflammatory and Angiogenic Factors.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Apr 30;11(5):899. doi: 10.3390/antiox11050899. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35624763 Free PMC article.
-
Thioredoxin: an antioxidant, a therapeutic target and a possible biomarker.Pediatr Res. 2024 Oct;96(5):1117-1119. doi: 10.1038/s41390-024-03370-6. Epub 2024 Jun 28. Pediatr Res. 2024. PMID: 38942889 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Mercier J.C., Hummler H., Durrmeyer X., Sanchez-Luna M., Carnielli V., Field D., Greenough A., Van Overmeire B., Jonsson B., Hallman M., et al. Inhaled nitric oxide for prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in premature babies (EUNO): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2010;376:346–354. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60664-2. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

