Capsosiphon fulvescens Glycoproteins Enhance Probiotics-Induced Cognitive Improvement in Aged Rats
- PMID: 32245093
- PMCID: PMC7146536
- DOI: 10.3390/nu12030837
Capsosiphon fulvescens Glycoproteins Enhance Probiotics-Induced Cognitive Improvement in Aged Rats
Abstract
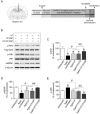
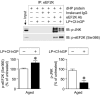
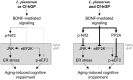
Aging-induced cognitive dysfunction can be regulated by probiotics through bidirectional communication with the brain. This study aimed to investigate whether Capsosiphon fulvescens glycoproteins (Cf-hGP) enhanced probiotic-induced improvement of memory in aged rats and the underlying mechanism in the dorsal hippocampus. Cf-hGP were isolated using lectin resin. Cf-hGP (15 mg/kg/day) and/or Lactobacillus plantarum (L. plantarum) (109 CFU/rat/day) were orally administered once a day for 4 weeks. Co-treatment with Cf-hGP and L. plantarum synergistically improved spatial memory in aged rats, which was overturned by functional blocks of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) signaling. Increases in BDNF expression and nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) phosphorylation were accompanied by mono- and/or co-administration in the dorsal hippocampus, while c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) phosphorylation and glucose-regulated protein 78 expression were decreased. These synergistic effects were downregulated by blocks of BDNF/Nrf2-mediated signaling. In particular, co-treatment, not mono-treatment, reduced phosphorylation of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 (eEF2) regulated by eEF2 kinase and protein phosphatase 2A. Additionally, co-treatment downregulated the interaction between eEF2 kinase and JNK. These data demonstrated that cognitive impairment in aged rats was synergistically diminished by co-treatment with Cf-hGP and L. plantarum through BDNF-mediated regulation of Nrf2 and eEF2 signaling pathways in the dorsal hippocampus.
Keywords: Capsosiphon fulvescens; aging-induced cognitive dysfunction; psychobiotics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hydrophilic Glycoproteins of an Edible Green Alga Capsosiphon fulvescens Prevent Aging-Induced Spatial Memory Impairment by Suppressing GSK-3β-Mediated ER Stress in Dorsal Hippocampus.Mar Drugs. 2019 Mar 15;17(3):168. doi: 10.3390/md17030168. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30875947 Free PMC article.
-
Glycoproteins of Capsosiphon fulvescens modulate synaptic clustering of PSD95 and prevent social isolation-induced cognitive decline in aged male rats.J Nutr Biochem. 2022 Sep;107:109054. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2022.109054. Epub 2022 May 21. J Nutr Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35609859
-
Impact of interval training with probiotic (L. plantarum / Bifidobacterium bifidum) on passive avoidance test, ChAT and BDNF in the hippocampus of rats with Alzheimer's disease.Neurosci Lett. 2021 Jun 21;756:135949. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2021.135949. Epub 2021 May 8. Neurosci Lett. 2021. PMID: 33974953
-
Molecular, histological and behavioral evidences for neuroprotective effects of minocycline against nicotine-induced neurodegeneration and cognition impairment: Possible role of CREB-BDNF signaling pathway.Behav Brain Res. 2020 May 27;386:112597. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2020.112597. Epub 2020 Mar 18. Behav Brain Res. 2020. PMID: 32198107
-
Long-Term Diet Supplementation with Lactobacillus paracasei K71 Prevents Age-Related Cognitive Decline in Senescence-Accelerated Mouse Prone 8.Nutrients. 2018 Jun 13;10(6):762. doi: 10.3390/nu10060762. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 29899283 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Neuroprotective Potentials of Marine Algae and Their Bioactive Metabolites: Pharmacological Insights and Therapeutic Advances.Mar Drugs. 2020 Jul 1;18(7):347. doi: 10.3390/md18070347. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32630301 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

