Synthesis, Characterization, and Optimization of Magnetoelectric BaTiO3-Iron Oxide Core-Shell Nanoparticles
- PMID: 32245105
- PMCID: PMC7153369
- DOI: 10.3390/nano10030563
Synthesis, Characterization, and Optimization of Magnetoelectric BaTiO3-Iron Oxide Core-Shell Nanoparticles
Abstract
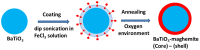
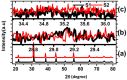
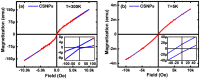
Improvement of magnetic, electronic, optical, and catalytic properties in cutting-edge technologies including drug delivery, energy storage, magnetic transistor, and spintronics requires novel nanomaterials. This article discusses the unique, clean, and homogeneous physiochemical synthesis of BaTiO3/iron oxide core-shell nanoparticles with interfaces between ferroelectric and ferromagnetic materials. High-resolution transmission electron microscopy displayed the distinguished disparity between the core and shell of the synthesized nanoparticles. Elemental mapping and line scan confirmed the formation of the core-shell structure. Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy detected the surface iron oxide phase as maghemite. Rietveld analysis of the X-ray diffraction data labeled the crystallinity and phase purity. This study provides a promising platform for the desirable property development of the futuristic multifunctional nanodevices.
Keywords: core–shell; energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy; magnetic iron-oxides; nanoparticles; oxide-nanomaterials synthesis; perovskite oxide; superparamagnetism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Morphology and electronic structure of the oxide shell on the surface of iron nanoparticles.J Am Chem Soc. 2009 Jul 1;131(25):8824-32. doi: 10.1021/ja900353f. J Am Chem Soc. 2009. PMID: 19496564
-
Synthesis, transfer, and characterization of core-shell gold-coated magnetic nanoparticles.MethodsX. 2019 Feb 8;6:333-354. doi: 10.1016/j.mex.2019.02.006. eCollection 2019. MethodsX. 2019. PMID: 30859070 Free PMC article.
-
A Detailed Investigation of the Onion Structure of Exchanged Coupled Magnetic Fe3-δO4@CoFe2O4@Fe3-δO4 Nanoparticles.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021 Apr 14;13(14):16784-16800. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c18310. Epub 2021 Mar 29. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021. PMID: 33780236
-
Mössbauer spectroscopic investigations on iron oxides and modified nanostructures: A review.J Mater Res. 2023;38(4):937-957. doi: 10.1557/s43578-022-00665-4. Epub 2022 Aug 29. J Mater Res. 2023. PMID: 36059887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exchange Bias Effects in Iron Oxide-Based Nanoparticle Systems.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2016 Nov 23;6(11):221. doi: 10.3390/nano6110221. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2016. PMID: 28335349 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Photocatalytic Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole, Nitenpyram and Tetracycline by Composites of Core Shell g-C3N4@ZnO, and ZnO Defects in Aqueous Phase.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Oct 4;11(10):2609. doi: 10.3390/nano11102609. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34685050 Free PMC article.
-
Strengthening Effect of Nb on Ferrite Grain Boundary in X70 Pipeline Steel.Materials (Basel). 2020 Dec 25;14(1):61. doi: 10.3390/ma14010061. Materials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33375580 Free PMC article.
-
Giant magnetoelectric coupling observed at high frequency in NiFe2O4-BaTiO3 particulate composite.RSC Adv. 2020 Jul 21;10(45):27242-27248. doi: 10.1039/d0ra05782g. eCollection 2020 Jul 15. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35515802 Free PMC article.
-
In silico assessment of electrophysiological neuronal recordings mediated by magnetoelectric nanoparticles.Sci Rep. 2022 May 19;12(1):8386. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-12303-4. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35589877 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling of core-shell magneto-electric nanoparticles for biomedical applications: Effect of composition, dimension, and magnetic field features on magnetoelectric response.PLoS One. 2022 Sep 23;17(9):e0274676. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0274676. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36149898 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mamun M.A.-A., Haque A., Pelton A., Paul B., Ghosh K. Structural, Electronic, and Magnetic Analysis and Device Characterization of Ferroelectric-Ferromagnetic Heterostructure (BZT-BCT/LSMO/LAO) Devices for Multiferroic Applications. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2018:1–8. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2018.2873513. - DOI
-
- Vopson M.M. Fundamentals of Multiferroic Materials and Their Possible Applications. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2015;40:223–250. doi: 10.1080/10408436.2014.992584. - DOI
-
- Haque A., Mahbub A.R., Abdullah-Al Mamun M., Reaz M., Ghosh K. Fabrication and thickness-dependent magnetic studies of tunable multiferroic heterostructures (CFO/LSMO/LAO) Appl. Phys. A. 2019;125:357. doi: 10.1007/s00339-019-2620-y. - DOI
-
- Zhao S. Advances in Multiferroic Nanomaterials Assembled with Clusters. J Nanomater. 2015:1. doi: 10.1155/2015/101528. - DOI
-
- Mamun M.A.-A., Haque A., Pelton A., Paul B., Ghosh K. Fabrication and ferromagnetic resonance study of BZT-BCT/LSMO heterostructure films on LAO and Pt. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019;478:132–139. doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.01.098. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

