Evaluation of Proinflammatory, NF-kappaB Dependent Cytokines: IL-1α, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α in Tissue Specimens and Saliva of Patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Oral Potentially Malignant Disorders
- PMID: 32245251
- PMCID: PMC7141524
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm9030867
Evaluation of Proinflammatory, NF-kappaB Dependent Cytokines: IL-1α, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α in Tissue Specimens and Saliva of Patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Oral Potentially Malignant Disorders
Abstract
Background: Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is a life-threatening disease. It could be preceded by oral potentially malignant disorders (OPMDs). It was confirmed that chronic inflammation can promote carcinogenesis. Cytokines play a crucial role in this process. The aim of the study was to evaluate interleukin-1alpha (IL-1α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-8 (IL-8), and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) in tissue specimens and saliva of patients with OSCC and OPMDs.
Methods: Cytokines were evaluated in 60 tissue specimens of pathological lesions (OSCCs or OPMDs) and in 7 controls (normal oral mucosa, NOM) by immunohistochemistry and in saliva of 45 patients with OSCC or OPMDs and 9 controls (healthy volunteers) by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays.
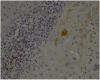
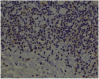
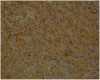
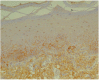
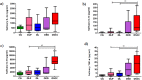
Results: Immunohistochemical analysis revealed significantly higher expression of IL-8 in OSCC specimens and TNF-α in OSCCs and OPMDs with dysplasia as compared to NOM. Moreover, expression of TNF-α was significantly higher in oral leukoplakia and oral lichen planus without dysplasia, whereas expression of IL-8 only in oral leukoplakia without dysplasia in comparison with NOM. Salivary concentrations of all evaluated cytokines were significantly higher in patients with OSCC than in controls. Moreover, levels of IL-8 were significantly higher in saliva of patients with OPMDs with dysplasia as compared to controls and in OSCC patients as compared to patients with dysplastic lesions. There was also significant increase in salivary concentrations of IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α in patients with OSCC as compared to patients with OPMDs without dysplasia.
Conclusion: The study confirmed that proinflammatory, NF-kappaB dependent cytokines are involved in pathogenesis of OPMDs and OSCC. The most important biomarker of malignant transformation process within oral mucosa among all assessed cytokines seems to be IL-8. Further studies on a larger sample size are needed to corroborate these results.
Keywords: biomarkers; cytokines; inflammation; oral potentially malignant disorders; oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The feasibility of monitoring NF-kappaB associated cytokines: TNF-alpha, IL-1alpha, IL-6, and IL-8 in whole saliva for the malignant transformation of oral lichen planus.Mol Carcinog. 2005 Oct;44(2):77-82. doi: 10.1002/mc.20113. Mol Carcinog. 2005. PMID: 16075467
-
Salivary and Serum Interleukin-6: A Credible Marker for Predicting Oral Leukoplakia and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA).Cureus. 2024 Apr 26;16(4):e59113. doi: 10.7759/cureus.59113. eCollection 2024 Apr. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38803729 Free PMC article.
-
Salivary Tumour Necrosis Factor-α as a Biomarker in Oral Leukoplakia and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2019 Jul 1;20(7):2087-2093. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2019.20.7.2087. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2019. PMID: 31350970 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in the Microenvironment of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OSCC) and Oral Potentially Malignant Disorders (OPMDs): Can They Shift Our Perspective? A Scoping Review.J Clin Med. 2025 Jan 18;14(2):606. doi: 10.3390/jcm14020606. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 39860614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress on the role of decorin in the development of oral mucosal carcinogenesis.Oncol Res. 2025 Feb 28;33(3):577-590. doi: 10.32604/or.2024.053119. eCollection 2025. Oncol Res. 2025. PMID: 40109852 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic polymorphisms and protein levels in vocal fold leukoplakia: a systematic review.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2022 Mar 11;55:e11920. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2022e11920. eCollection 2022. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2022. PMID: 35293553 Free PMC article.
-
Correlations between Salivary Immuno-Biochemical Markers and HbA1c in Type 2 Diabetes Subjects before and after Dental Extraction.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Oct 30;10(11):1741. doi: 10.3390/antiox10111741. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34829612 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of salivary biomarker interleukin-6 in oral squamous cell carcinoma and oral potentially malignant disorders - A comparative cross-sectional South Indian study.J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2024 Jul-Sep;28(3):387-392. doi: 10.4103/jomfp.jomfp_122_24. Epub 2024 Oct 15. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2024. PMID: 39670140 Free PMC article.
-
Peroxiredoxin 1 Promotes Proinflammatory Cytokine Secretion in Human Dysplastic Oral Keratinocytes and Mouse Tongue Precancerous Tissues.Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2025 Mar 30;2025:6577043. doi: 10.1155/ancp/6577043. eCollection 2025. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2025. PMID: 40196418 Free PMC article.
-
IL-1 Generated by Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Stimulates Tumor-Induced and RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis: A Possible Mechanism of Bone Resorption Induced by the Infiltration of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 30;24(1):688. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010688. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36614130 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Johnson N.W., Warnakulasuriya S., Gupta P.C., Dimba E., Chindia M., Otoh S.C., Sankaranarayaranan R., Califano J., Kowalski L. Global oral health inequalities in incidence and outcomes for oral cancer: Causes and solutions. Adv. Dent. Res. 2011;23:237–246. doi: 10.1177/0022034511402082. - DOI - PubMed
-
- El-Naggar A.K., Chan J.K.C., Grandis J.R., Takata T., Slootweg P.J. WHO Classification of Head and Neck Tumours. 4th ed. International Agency for Research on Cancer; Lyon, France: 2017. pp. 105–131.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

