Trends in anticoagulant prescribing: a review of local policies in English primary care
- PMID: 32245380
- PMCID: PMC7126454
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-020-5058-1
Trends in anticoagulant prescribing: a review of local policies in English primary care
Abstract
Background: Oral anticoagulants are prescribed for stroke prophylaxis in patients with atrial fibrillation, which is the most common heart arrhythmia worldwide. The vitamin K antagonist (VKA) warfarin is a long-established anticoagulant. However, newer direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) have been recently introduced as an alternative. Given the prevalence of atrial fibrillation, anticoagulant choice has substantial clinical and financial implications for healthcare systems. In this study, we explore trends and geographic variation in anticoagulant prescribing in English primary care. Because national guidelines in England do not specify a first-line anticoagulant, we investigate the association between local policies and prescribing data.
Methods: Primary care prescribing data of anticoagulants for all NHS practices from 2014 to 2019 in England was obtained from the ePACT2 database. Public formularies were accessed online to obtain local anticoagulation prescribing policies for 89.5% of clinical commissioning groups (CCGs). These were categorized according to their recommendations: no local policies, warfarin as first-line, or identification of a preferred DOAC (but not a preferred anticoagulant). Local policies were cross-tabulated with pooled prescribing data to measure the strength of association with Cramér's V.
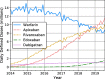
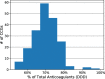
Results: Nationally, prescribing of DOACs increased from 9% of all anticoagulants in 2014 to 74% in 2019, while that of warfarin declined accordingly. Still, there was significant local variation. Across geographical regions, DOACs ranged from 53 to 99% of all anticoagulants. Most CCGs (73%) did not specify a first-line choice, and 16% recommended warfarin first line. Only 11% designated a preferred DOAC. Policies with a preferred DOAC indeed correlated with increased prescribing of that DOAC (Cramér's V = 0.25, 0.27, 0.38 for rivaroxaban, apixaban, edoxaban respectively). However, local policies showed a negligible relationship with the classes of anticoagulants prescribed-DOAC or VKA (Cramér's V = 0.01).
Conclusions: Nationally, the use of DOACs to treat atrial fibrillation has increased rapidly. Despite this, significant geographical variation in uptake remains. This study provides insights on how local policies relate to this variation. Our findings suggest that, in the absence of a nationally recommended first-line anticoagulant, local prescribing policies may aid in deciding between individual DOACs, but not in adjudicating between DOACs and vitamin K antagonists (i.e. warfarin) as general classes.
Keywords: DOAC; England; NOAC; anticoagulant; atrial fibrillation; local policy; prescribing; primary care; stroke; warfarin.
Conflict of interest statement
GL is the Deputy Chief Executive at the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. MvH was a clinical fellow at NICE, and KHH was a summer intern at NICE.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

