Intranasal epinephrine effects on epinephrine pharmacokinetics and heart rate in a nasal congestion canine model
- PMID: 32245384
- PMCID: PMC7119008
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-020-01343-x
Intranasal epinephrine effects on epinephrine pharmacokinetics and heart rate in a nasal congestion canine model
Abstract
Background: Histamine release and vasodilation during an allergic reaction can alter the pharmacokinetics of drugs administered via the intranasal (IN) route. The current study evaluated the effects of histamine-induced nasal congestion on epinephrine pharmacokinetics and heart rate changes after IN epinephrine.
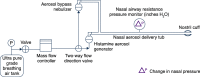
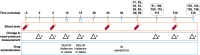
Methods: Dogs received 5% histamine or saline IN followed by 4 mg epinephrine IN. Nasal restriction pressure, epinephrine concentration, and heart rate were assessed. Maximum concentration (Cmax), area under plasma concentration-time curve from 1 to 90 min (AUC1-90), and time to reach Cmax (Tmax) were measured. Clinical observations were documented.
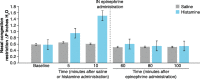
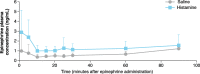
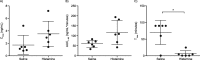
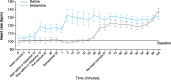
Results: In the 12 dogs in this study, nasal congestion occurred at 5-10 min after IN histamine administration versus no nasal congestion after IN saline. After administration of IN epinephrine, IN histamine-mediated nasal congestion was significantly reduced to baseline levels at 60, 80, and 100 min. There were no significant differences in Cmax and AUC1-90 between histamine and saline groups after IN epinephrine delivery (3.5 vs 1.7 ng/mL, p = 0.06, and 117 vs 59 ng/mL*minutes, p = 0.09, respectively). After receiving IN epinephrine, the histamine group had a significantly lower Tmax versus the saline group (6 vs 70 min, respectively; p = 0.02). Following IN epinephrine administration, the histamine group showed rapidly increased heart rate at 5 min, while there was a delayed increase in heart rate (occurring 30-60 min after administration) in the saline group. Clinical observations included salivation and emesis.
Conclusion: IN histamine led to more rapid epinephrine absorption and immediately increased heart rate compared with IN saline. IN epinephrine decreased histamine-induced nasal congestion.
Keywords: Allergy; Anaphylaxis; Epinephrine; Histamine; Intranasal; Nasal congestion; Severe allergy; Vasodilation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of Intranasal Epinephrine on Cerebrospinal Fluid Epinephrine Pharmacokinetics, Nasal Mucosa, Plasma Epinephrine Pharmacokinetics, and Cardiovascular Changes.Pharm Res. 2020 May 24;37(6):103. doi: 10.1007/s11095-020-02829-5. Pharm Res. 2020. PMID: 32448925
-
Intranasal epinephrine in dogs: Pharmacokinetic and heart rate effects.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2020 Apr;8(2):e00587. doi: 10.1002/prp2.587. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2020. PMID: 32302068 Free PMC article.
-
Randomized trial of pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic effects of 13.2 mg intranasal epinephrine treatment in congestion.Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2024 Aug;133(2):186-193.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2024.04.033. Epub 2024 May 7. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38719149 Clinical Trial.
-
The pathophysiology, clinical impact, and management of nasal congestion in allergic rhinitis.Clin Ther. 2008 Apr;30(4):573-86. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2008.04.011. Clin Ther. 2008. PMID: 18498908 Review.
-
Allergic Rhinitis: A Review.JAMA. 2024 Mar 12;331(10):866-877. doi: 10.1001/jama.2024.0530. JAMA. 2024. PMID: 38470381 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging Therapies in Anaphylaxis: Alternatives to Intramuscular Administration of Epinephrine.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2021 Mar 5;21(3):18. doi: 10.1007/s11882-021-00994-0. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2021. PMID: 33666759 Review.
-
Exploring the anti-anaphylaxis potential of natural products: A Review.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 May;33(5):2589-2622. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01685-2. Epub 2025 Mar 19. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40106030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of neffy, an Epinephrine Nasal Spray, for Severe Allergic Reactions.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jun 14;16(6):811. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16060811. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38931932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of anaphylaxis on the absorption of intranasal epinephrine in anaesthetized non-naive beagle dogs.J Allergy Clin Immunol Glob. 2023 Aug 30;2(4):100165. doi: 10.1016/j.jacig.2023.100165. eCollection 2023 Nov. J Allergy Clin Immunol Glob. 2023. PMID: 38024850 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetics of intravenous, oral transmucosal, and intranasal buprenorphine in healthy male dogs.J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Jul;45(4):358-365. doi: 10.1111/jvp.13056. Epub 2022 Apr 21. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35445748 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

