Primary stratification and identification of suspected Corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19) from clinical perspective by a simple scoring proposal
- PMID: 32245395
- PMCID: PMC7125053
- DOI: 10.1186/s40779-020-00246-8
Primary stratification and identification of suspected Corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19) from clinical perspective by a simple scoring proposal
Abstract
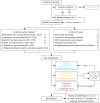
In this Commentary, we would like to comment on the article titled "A rapid advice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infected pneumonia (standard version)" as a featured article in Military Medical Research. In the guideline, except for "confirmed cases", "suspected cases", "close contact" and "suspicious exposure" were defined by clinical perspective based on epidemiological risk, clinical symptoms and auxiliary examination. Combined with our experience, we introduced a simple scoring proposal additionally based on not only CT imaging as strongly recommended by the guideline but also blood routine test, especially for primary screening of such patients in the out-patient department.
Keywords: Blood test; COVID-19; CT imaging; Primary screening; Suspected cases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Updating the diagnostic criteria of COVID-19 "suspected case" and "confirmed case" is necessary.Mil Med Res. 2020 Apr 4;7(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s40779-020-00245-9. Mil Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32245396 Free PMC article.
Comment on
-
A rapid advice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infected pneumonia (standard version).Mil Med Res. 2020 Feb 6;7(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s40779-020-0233-6. Mil Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32029004 Free PMC article.
References
-
- National Health Protection Committee. [Novel coronavirus pneumonia diagnosis and treatment plan (Trial Seventh Edition)]. 2020. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/yzygj/s7653p/202003/46c9294a7dfe4cef80dc7f5912eb19.... Accessed 5 Mar 2020.
-
- WHO. Coronavirus disease (COVID-2019) situation reports. 2020. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio.... Accessed 18 Mar 2020.
-
- Guan WJ, Ni Z, Hu Y, Liang WH, Ou CQ, He JX, et al. Clinical characteristics of 2019 novel coronavirus infection in China. medRxiv. 2020. 10.1101/2020.02.06.20020974:2020.02.06.20020974.
-
- Li ZH, Gao XL, Yang XJ, Xu H. [The interference factors in Coronavirus 2 nucleic acid detection]. 2020. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/50.1167.R.20200317.1710.002.html. Accessed 5 Mar 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources