Cerebrospinal fluid p-tau217 performs better than p-tau181 as a biomarker of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 32246036
- PMCID: PMC7125218
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-15436-0
Cerebrospinal fluid p-tau217 performs better than p-tau181 as a biomarker of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
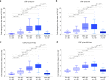
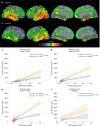
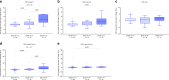
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) p-tau181 (tau phosphorylated at threonine 181) is an established biomarker of Alzheimer's disease (AD), reflecting abnormal tau metabolism in the brain. Here we investigate the performance of CSF p-tau217 as a biomarker of AD in comparison to p-tau181. In the Swedish BioFINDER cohort (n = 194), p-tau217 shows stronger correlations with the tau positron emission tomography (PET) tracer [18F]flortaucipir, and more accurately identifies individuals with abnormally increased [18F]flortaucipir retention. Furthermore, longitudinal increases in p-tau217 are higher compared to p-tau181 and better correlate with [18F]flortaucipir uptake. P-tau217 correlates better than p-tau181 with CSF and PET measures of neocortical amyloid-β burden and more accurately distinguishes AD dementia from non-AD neurodegenerative disorders. Higher correlations between p-tau217 and [18F]flortaucipir are corroborated in an independent EXPEDITION3 trial cohort (n = 32). The main results are validated using a different p-tau217 immunoassay. These findings suggest that p-tau217 might be more useful than p-tau181 in the diagnostic work up of AD.
Conflict of interest statement
S.J., E.S., S.P., N.M. declare no competing interests. Ru.S. has served as a non-paid consultant for Roche. O.H. has acquired research support (for the institution) from Roche, GE Healthcare, Biogen, AVID Radiopharmaceuticals and Euroimmun. In the past 2 years, he has received consultancy/speaker fees (paid to the institution) from Biogen and Roche. J.L.D., N.K.P., X.C., D.C.A., J.R.S., S.S. are employees of Eli Lilly and Company. G.T.B., C.T., Ra.S., M.M., H.K. are employees of Janssen R&D.
Figures
References
-
- Scheltens P, et al. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet. 2016;388:505–517. - PubMed
-
- Alonso AD, Beharry C, Corbo CP, Cohen LS. Molecular mechanism of prion-like tau-induced neurodegeneration. Alzheimers Dement. 2016;12:1090–1097. - PubMed
-
- Hanger DP, Anderton BH, Noble W. Tau phosphorylation: the therapeutic challenge for neurodegenerative disease. Trends Mol. Med. 2009;15:112–119. - PubMed
-
- Olsson B, et al. CSF and blood biomarkers for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15:673–684. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

